Finance 331: Principles of Financial Management
advertisement
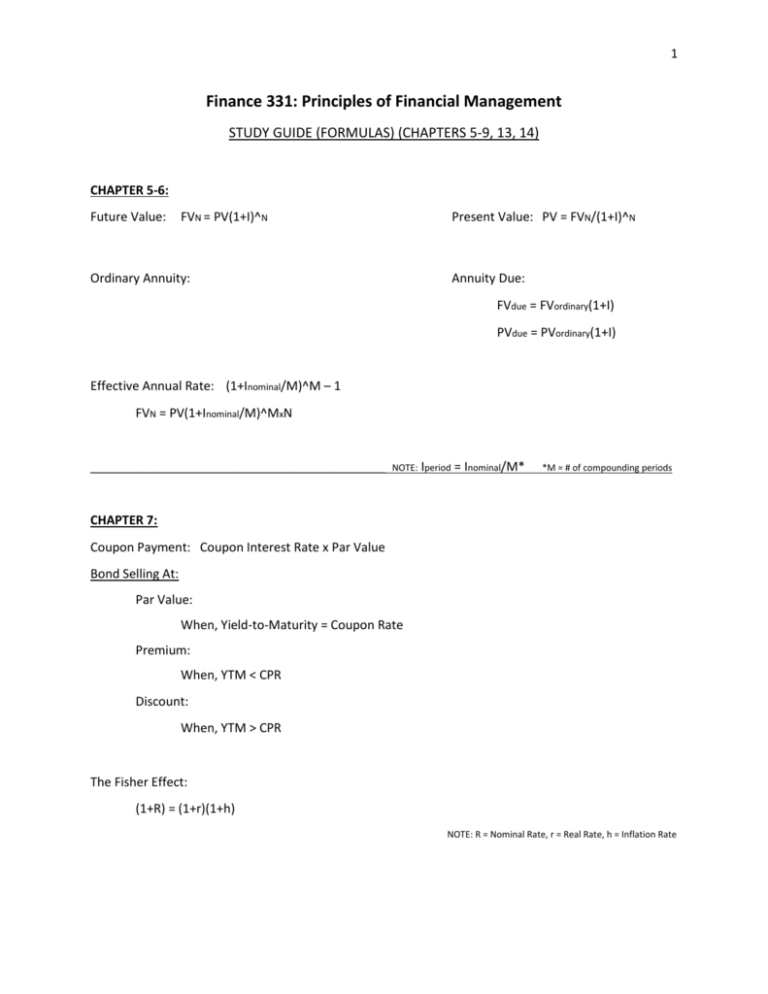
1 Finance 331: Principles of Financial Management STUDY GUIDE (FORMULAS) (CHAPTERS 5-9, 13, 14) CHAPTER 5-6: Future Value: FVN = PV(1+I)^N Present Value: PV = FVN/(1+I)^N Ordinary Annuity: Annuity Due: FVdue = FVordinary(1+I) PVdue = PVordinary(1+I) Effective Annual Rate: (1+Inominal/M)^M – 1 FVN = PV(1+Inominal/M)^MxN ___________________________________________ NOTE: Iperiod = Inominal/M* *M = # of compounding periods CHAPTER 7: Coupon Payment: Coupon Interest Rate x Par Value Bond Selling At: Par Value: When, Yield-to-Maturity = Coupon Rate Premium: When, YTM < CPR Discount: When, YTM > CPR The Fisher Effect: (1+R) = (1+r)(1+h) NOTE: R = Nominal Rate, r = Real Rate, h = Inflation Rate 2 CHAPTER 8: Computing Future Dividends: Constant Dividends: Constant Growth Rate: P0 = [D0(1+g)/R-g] = D1/R-g P0 = D/R Non-Constant Growth: -Use Timeline -Find Future Dividend and Price -Find PV of each then ADD R = [D0(1+g)/P0]+g = [D1/P0] +g Value of a Perpetuity: P0 = D/R Pt = Benchmark PE Ratio x Earnings-Per-Share or Pt = Benchmark Price-Sales Ratio x Sales-Per-Share NOTE: Compute the future dividend stream based on the dividend growth rate (if using a timeline). Use the dividend growth model to determine the price of the stock.__________________________________________________________________________________________ CHAPTER 9: Technique Payback Discounted Payback Net Present Value Internal Rate of Return Units Time Time Money ($) Percentage (%) Accept if Payback < Management’s # Payback < Management’s # NPV > $0 IRR > R (Required Return) Mutually Exclusive Projects: Choose project with the higher NPV or (if NPV is not used) choose project with the higher IRR. If there is a conflict between NPV and another decision rule, you should always use NPV. NPV directly measures the increase (or decrease) in value the project provides to the firm. 3 CHAPTER 13: Return: [Expected Ending Value – Cost /Cost] Expected Return: (The sum of each return times their respective probabilities) Coefficient of Variation: CV = (Variance/Expected Return), measures the risk per unit of return Stand-Alone Risk (Total Risk): = Market Risk (Systematic Risk, measured by Beta) + Diversifiable Risk (Unsystematic Risk, measured by Standard Deviation) Beta: Measures stock’s market risk by showing the volatility relative to the market Indicates how risky a stock is if the stock is held in a well-diversified portfolio Capital Asset Pricing Model: Expected Return = Risk-Free Rate + (Market Return – Risk-Free Rate) x Beta _____________________________________________________________________________________ CHAPTER 14: Weighted Average Cost of Capital: Cost of Equity: P0 = D1/R-g R = D1/P0 + g Cost of Preferred Stock: P0 = D/RPS Cost of Debt: or R = Risk-Free Rate + (RM – RF) x Beta RPS = D/P0 Yield-to-Maturity Equity Market Weight/Value: Number of shares outstanding x the market price of one share Debt Market Weight/Value: Number of bonds outstanding x the market price of one bond WACC: WACC = (Weight of Equity x Return of Equity) + (Weight of Preferred Stock x Return of Preferred Stock) + [(Weight of Debt x (Return of Debt)(1 – Tc)] Note: Use after-tax cost of debt = Rd(1 – Tc), where Tc is corporate tax rate











