The Body Systems - Boone County Schools
advertisement

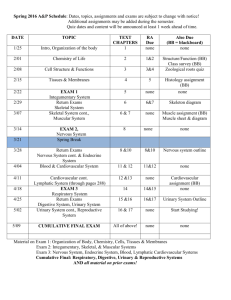
The different systems of the Human Body What is a Body System? A body system is a group of organs that work together to perform a main body function Nervous System Skeletal System Muscular System Endocrine System Digestive System Cardiovascular System Immune System Respiratory System Urinary System Reproductive System Nervous System (NOTES) Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Made up of the brain and the spinal cord Made up of the nerve cells that branch out to the muscles, skin, internal organs, and glands The brain is the control center of the body Protecting the Nervous System (NOTES) To protect the Nervous System: Wear a protective helmet Avoid diving in shallow water Wear a seatbelt Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system transports nutrients, gases, hormones, and cellular waste throughout the body Biggest duty of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood (NOTES) Cardiovascular System (NOTES IN RED) The cardio system consists of 3 parts: 1. Blood Red Blood Cells-transport oxygen White Blood Cells- prevent infection 2. Blood Vessels Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries 3. Heart – four chambered muscle that pumps blood throughout the body Protecting the Cardio System To protect the Cardiovascular System: Reduce the fat in your diet Reduce the amount of salt in your diet Exercise regularly Avoid tobacco products (can increase blood pressure) Maintain a healthy weight Practice stress management Skeletal System (NOTES) Skeletal system is the framework of the human body 206 bones in the human body Largest bone is femur Protect important organs Protecting the Skeletal System To protect the Skeletal System: Eat calcium foods Use good posture Get checked for scoliosis Wear proper fitting shoes Wear protective gear when playing sports Muscular System Muscular system consists of muscles that provide motion and maintain posture Speed: slow twitch and fast twitch muscles Control: voluntary and involuntary muscles There are 3 main types of muscles: (NOTES) Smooth muscles Skeletal muscles Cardiac Muscles Protecting the Muscular System To protect the Muscular System: Stop exercising if injured Warm up and stretch before exercise Maintain proper weight Lift object with knees Sleep on a firm mattress Digestive System The digestive system breaks food down into nutrients that can be used by the body The digestive system includes: Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Liver The liver releases bile to breakdown fat, maintain blood sugar level, and filter wastes Protecting the Digestive System To protect the Digestive System: Eat slowly Eat foods with plenty of fiber Practice stress management skills to avoid indigestion Drink plenty of water Respiratory System The respiratory system provides body cells with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide that cells produce as waste The lungs are main organs of the respiratory system (NOTES) Protecting the Respiratory System To protect the Respiratory System: Do not smoke Avoid secondhand smoke Do not inhale harmful drugs or chemicals Exercise regularly Avoid polluted areas Immune System The immune system removes harmful organism from the blood and fights pathogens White Blood cells plays a huge part of the immune system (NOTES) Protecting the Immune System To protect the Immune System: -get plenty of rest and sleep -get plenty of vitamins -get immunizations -seek medical help if needed -exercise -avoid drugs Urinary System The urinary system removes harmful liquid wastes from the body and maintains the body’s water balance Consists of the kidneys, Bladder, Urethra, and Uterus DRINK A LOT OF WATER Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that control many of the body’s activities by producing hormones A hormone is a chemical messenger that is released directly into the bloodstream Glands include the Pituitary gland, Thyroid gland, Pancreas, and Adrenal gland Protecting the Endocrine System To protect the Endocrine System: Have regular checkups Males check for testicular cancer Females keep track of menstrual cycle Reproductive System