Medical Terminology - Porterville College
advertisement

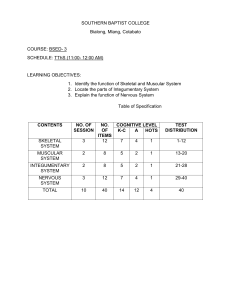
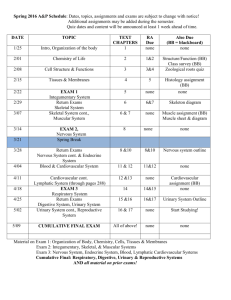
Medical Terminology List 4 Chapter 2 Cells • Basic functional unit of the body Tissue • Groups of cells • Working together • To perform a specialize function Organ • Composed to 2 or more different types of tissue • Specific function • Usually recognizable shape System • Related organs • Common function Organism • Collection of body systems • Make up the most complex level of life Body Systems -11 • Circulatory System • Lymphatic (immune) system • Digestive system • Endocrine system • Reproductive system • Muscular system • • • • • Skeletal system Nervous system Respiratory system Integumentary system Urinary system Circulatory System • Contains – Heart, Arteries; Veins; Capillaries; Blood; Spleen • Function – to deliver oxygenated blood to the body Lymphatic (Immune) System • Contains – Lymph nodes, white blood cells • Function – to remove infectious diseases and other pathogens from the human body Digestive System • Contains – Mouth, Esophagus, Stomach, Pancreas, Liver, Gallbladder, Intestines • Function – To convert food particles into simpler, molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Endocrine System • Contains: Glands – – – – – – – – hypothalamus pituitary gland thyroid parathyroid adrenal glands pancreas testes ovaries Endocrine System • Function – to control growth, development, metabolism and reproduction through the production and secretion of hormones Reproductive System • Contains – Female: Ovaries, uterus, vagina – Male: Testis, penis, prostate • Function – Allows for the continuation of the human species Muscular System • Contains – Muscles • Function – works with the skeletal and nervous system to produce movement Skeletal System • Contains – Bones – Femur, humerus, radius and ulna, cranium, fibula and tibia, vertebrae, pelvic bone, phalanges • Function – to provide structure and support to the body Nervous System • Contains – Brain, spinal cord, nerves • Function – to coordinate the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environment Respiratory System • Contains – Nose, Pharynx, Larynx, Trachea, Bronchi, alveoli, lungs, diaphragm • Function – to provide the body with a oxygen and remove carbon dioxide Integumentary System • Contains – Skin • Function – protection to the underlying layers – body temperature regulation – nerves that respond to temperature, touch, pressure, and pain Urinary System • Contains – Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra • Function – Remove waste products from the body – Keep fluid and electrolyte levels normal Circul/a • circle Crin/o • secrete Muscul/o • muscle Pulmon/o • lung Skelet/o • Skeleton, bone Ur/o • urine -ar • Pertaining to -ary • Pertaining to (process) -ation • Process, condition -crine • secretion -graph • Instrument to record -ive • The adjective form of a noun -tive • The adjective form of a noun -uria • Urine condition -y • Condition, process