Section 2 Cell Division PP
advertisement

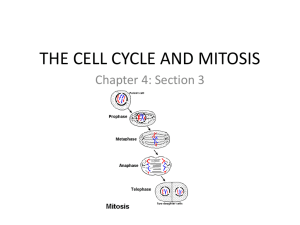
Section 2 Cell Division Cell Division: The process by which cells produce offspring cells. All cells come from preexisting cells. Cell division differs in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Cell reproduction: 1 cell makes 2 cells. 25 million cells per second are produces by an adult human. Cell Division in Prokaryotes Cell division in prokaryotes is called Binary Fission. Binary Fission one cell makes two cells. Example: Bacteria Process: Cell Division in Prokaryotes Cell Division in Eukaryotes Both the cytoplasm and the nucleus divide. Mitosis: Cell division that results in cells with identical genetic material as the original cell. The cell Cycle: The repeating set of events in the life of the cell. Steps in the cell cycle Interphase: Time between cell divisions. Cells are growing in size. Mitosis: The nucleus of the cell divides. Cytokinesis: The division of the cell’s cytoplasm. Interphase G1 Cell Growth S –DNA is copied G2 Cell grows and prepares for cell division. G 0 Exit the cell cycle and do not copy their DNA. Steps of the cell cycle Mitosis: Division of the nucleus. Divided into four phases. Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telephase. Prophase (Step 1) First stage of mitosis. Shortening and tight coiling of DNA into rodshaped chromosomes. Centrosomes appear and separate. Spindle fibers radiate from the centrosomes. Metaphase(Step 2) Second stage Kinetochore fibers move the chromosomes to the center of the cell. Anaphase(Step 3) 3rd stage Chromatids of each chromosome separate at the centromere and move toward opposite poles of the dividing cell. Telophase th (4 step) 4th stage Spindle fibers disassemble Chromosomes become less tightly coiled Chromatin state Nuclear envelope forms. Cytokinesis Cells start to divide. Cell membrane pinches in and separate the cell into TWO cells. Cytokinesis in plants form a cell plate. Cell plate becomes the cell wall. Control of cell division Cell growth(G1) check point: If the cell is healthy it will go to DNA synthesis. If the cell is not big enough or unhealthy it will stay in G0 phase. DNA synthesis((G2) Checkpoint: If the cell is copied correctly it will go to the next step. If not it will stop. Mitosis checkpoint: Checks to make sure the cell divides correctly. Control is lost: Cancer If mutation occurs the cell will not grow or divide properly. This will lead to cancer. Cancer cells do not respond to the body’s control mechanisms. Results in overproduction of damaged cells.