Cell Cycle and Mitosis Study Guide
advertisement

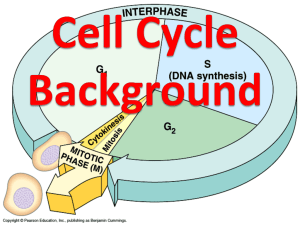
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Study Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. List 2 reasons why cells divide? Reproduce and repair Describe the chromosome structure of a bacteria. Circular The region of a chromosome where two sister chromatids are held together is called a __centromere________. Describe the structure of a chromosome. In order to fit within a cell, DNA becomes more compact by wrapping around _proteins called histones__. In a bacterium , what type of cell division takes place? What is the result? Binary fission, results in two identical cells The phase of the cell cycle that occupies most of an average cell’s life is interphase_. What phase does the cell enter after cytokinesis is completed? interphase Which of the following shows the correct sequence of the cell cycle? A. Cytokinesis mitosisG1S G2 B. SG1G2mitosiscytokinesis C. G1SG2mitosiscytokinesis D. MitosisG1SG2cytokinesis Cells that are not dividing remain in which phase? interphase The synthesis (S) phase is characterized by what process? Replication of DNA The first three steps of the cell cycle are collectively known as Interphase_. Mitosis is the process by which cells divide__. The phase of mitosis that is characterized by the arrangement of all chromosomes along the equator/middle of the cell is called metaphase_____. Use the picture below to answer questions 17-19 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. The cell is picture 1 is in what phase of mitosis__anaphase. The cell in picture 2 is in what phase of mitosis? _prophase___. The cell in picture 5 is in what phase of mitosis? _telophase_. Using the numbers that correspond with the pictures above put the events of mitosis in order? 2,4,3,1,5 As a result of mitosis, each of the two new cells produced from the parent cell during cytokinesis are identical to the parent cell. Cytokinesis in plant cells involves the formation of _cell plate_ , while in animal cells a _cleavage furrow__ forms. What aids the chromosomes to line up in the middle (equator) of the cell? Spindle fibers What organelle do animal cells have that plant cells do not have when undergoing mitosis?centrioles Which cells undergo binary fission as their form of replication? bacteria The cells that undergo asexual reproduction produce cells that are identical to the parent cells 25. 26. 27. 28. The structure labeled A in the figure above is called the centromere. The structure labeled B in the figure above are called chromatid. Together the G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase are called _interphase____. The structure labeled A in the figure below is called the cell plate 29. What is the process that directly follows telophase in the cell cycle? cytokinsis 30. In all forms of _cancer_____, the cancerous cells fail to respond to the signals that regulate the cell cycle of most cells 31. The DNA in eukaryotic cells is packaged into structures called chromosomes__. 32. What stage of mitosis do chromosomes condense and become visible? prophase 33. What happens to the amount of DNA in a cell as it moves through one cell cycle? It doubles at first then divides 34. This is controlled cell death apoptosis 35. What things can affect the rate of the cell cycle? Age of cell, exposure to radiation, and infection of a virus 36. Describe the structure of DNA. Double stranded/ double helix 37. Describe the structure of RNA. Single stranded 38. Name the 3 parts of a nucleotide. Sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen base What are 2 differences in DNA and RNA nuceotides? In RNA the sugar is ribose and in DNA it is Deoxyribose. In RNA Uracil is present and pairs with adenine and in DNA thymine pairs with adenine 39. What 4 nucleotide bases does DNA contain? Adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine What 4 nucleotide bases does RNA contain? Adenine, uracil, cytosine and guanine 40. A picture of chromosomes that allow for a person’s chromosomes to be closely study is called a karyotype. 41. What is DNA’s main role in storing and transmitting genetic information (Hint; think translation). It serves as a template for the production of proteins 42. Transcribe the following DNA code into mRNA: TAA-GCC-TAT-TCC AUU-CGG-AUA-AGG 43. What is the role/function of mRNA? It takes the message held In DNA out of the nucleus to the ribosome 44. What is the role/function of tRNA? tRNA brings the amino acid to the ribosome to make the protein 45. Describe the purpose of transcription. The purpose of transcription is to construct an RNA strand from a DNA strand. 46. Describe the purpose of translation. The purpose of translation is to convert the genetic code in RNA into an amino acid sequence to make a protein 47. Using your genetic code chart translate the following mRNA sequence: GUC-ACC-GAG-CGC-UGC Valine, threonine, glutamic acid, arginine, cysteine