22.4 Plant Notes
advertisement

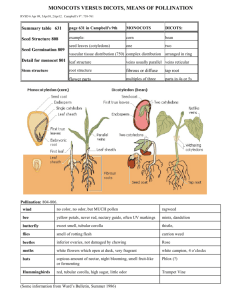
22.4 FLOWERING PLANTS Flowers & Fruits Angiosperm – make up the vast majority of plant species Reproductive organs are called flowers Flowers contain ovaries which surround & protect the seeds Reproduce sexually by means of flowers After fertilization, ovaries within the flowers develop into fruit Fruit surround, protect, and help disperse seeds Advantages of Flowers Attract animals Drawn by color, scent, or shape Pollination by animal/insect is much more efficient than by wind Advantages of Fruit A structure containing one or more matured ovaries Fruit wall helps disperse the seeds inside it Animal eats the fruit, digests it, and has traveled by the time it eliminates it Angiosperm Classification Monocots – embryos with 1 seed leaf (single group) Dicots – embryos with 2 seed leaves (placed in a variety of different catagories) And can’t be used for classification anymore Angiosperm Diversity Often grouped according to the number of their seed leaves, strength and composition of their stem, & number of growing seasons they live Monocots & Dicots Monocots (corn, wheat, lilies, orchids, and palms) o First plants to be grown in mass quantities for food o Single cotyledon (seed leaves), parallel veins, flowers in multiples of 3, vascular bundles scattered throughout the stem, and fibrous roots Dicots ( roses, clover, tomatoes, oaks, and daisies) 2 cotyledon, branched veins, floral parts in multiples or 4 or 5, vascular bundles arranged in a ring, tap roots Woody & Herbaceous Plants (stem characteristics) Woody plants have cells with thick cell walls that support the plant body (trees, shrubs, and vines) Herbaceous plants do not produce wood as they grow (dandelions, zinnias, petunias, sunflowers) Annuals, Biennials & Perennials Annuals grow from seed to maturity, flower, produce seed and die in 1 year Biennials sprout and grow short stems and some leaves in 1st year, grow new stems & leaves, flower, produce seeds and die in 2nd year Perennials-most have woody stems, die each winter and are replaced in the spring