Pollination_SeedToFlower

Plant Reproduction…
Fruits and Seeds
(Take notes on Underlined Information)
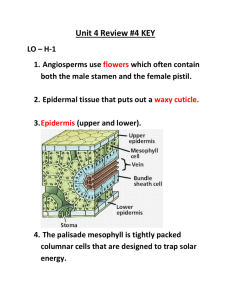
We already looked at the flower
Pollen (plant sperm)
Pollen Dispersal
Animals
usually barbed or sticky
Bees, Flies, etc
80% of pollination
Mammals
Birds
Wind
usually light & aerodynamic
Water
for plants that grow underwater eg. Eelgrass
Pollination (Fertilization)
Pollen sticks to the sticky substance on the stigma
The sperm break out and create a pollen tube
Every fruit requires two sperm – one to fertilize the embryo and one to fertilize the endosperm
(food for the embryo)
Pollen Tube Formation
Pollen swells from moisture on stigma
Pollen tube grows so that sperm can reach the egg
200-300 nm/second growth
Fastest growing cell type known
(Yellow pollen in picture is a different species that won’t be allowed to reach the egg cells.)
What is a Seed?
A seed is the reproductive unit of a flowering plant. From a reproductive point of view, a seed has the “baby” plant inside.
Seed Dispersal
Dispersal: Species movement away from an existing population or away from the parent organism
Animal dispersal
Most birds lack sensitive noses and are much more reliant on color when finding food – red, hot pink, orange.
Insects can have excellent senses of smell or color vision or both – especially like blues, yellows and purples.
Some fruits contain a laxative that ensures that the seed will be released from the digestive tract fairly quickly.
Seed Dispersal…
Wind
Usually light (low density) & aerodynamic
May have wings
Sycamore Seed
Water
For plants that grow in or near large bodies of water (eg. Coconut)
Wood Hawthorne Seed
Density less than that of water so they can float
Must be somewhat waterproof
Surf grass Seed
What is a Fruit?
Fruit is the enlarged ovary and any other floral part that undergoes a post-pollination development
Fruits are what is left of the flower after pollination
What is a Nut?
A nut is a hard fruit with a seed inside.
The nutshell, technically, is the fruit.
The part we eat is the seed.
So many examples…
Each lab station contains pictures and detailed information on various seeds, fruits and nuts.
(Spend about 2-3 minutes at each station)
Coconut
Some scientists like to refer to the coconut as a water dispersal fruit and seed.
If you look at one end of the coconut, you’ll see three pores.
The coconut seed germinates and a shoot emerges from one of the pores.
In addition to the “baby” plant in the seed, there is the food to kick off its life called the endosperm.
The endosperm is what makes up most of the seed and, in the coconut’s case, is the yummy white stuff we eat.
Flower
Pomegranate
(Leathery Berry)
The name pomegranate derives form Middle
French, pomme garnete, literally "seeded apple”
Pomegranates contain
840 arils “seeds” that are compartmentalized.
As the flower dries up, the base of the flower
(now fertilized) swells into the berry we know.
Look closely at the end you can see the dried up stamen
Buckeye (Capsule)
Hummingbirds pollinate this tree.
Flowers are poisonous to honey bees!
The seeds are poisonous to humans when raw.
Coast Live Oak
(Nut)
The chances of one acorn making it to become an oak tree are very slim -- less than 1/10,000
Acorns are eaten by squirrels, birds, deer and woodpeckers.
Birch (Catkin)
Fruit is called a winged nutlet.
Used by native
Americans to make canoes and other tools.
Birds, rabbits and rodents feed on the bark and seeds.
Immature Catkin
Flower
Mature Catkin
Magnolia
(Aggregate Follicle)
Aggregate fruit that is woody.
Not a cone like pine.
They are typically pollinated by beetles.
They don’t produce any nectar that bees and birds would like but the beetles eat the pollen which is high in protein.
Most primitive flowering tree.
Carob (Pod)
Carob pods are processed to a cocoa -like flour and are sometimes used as a chocolate substitute
Significant odor (go ahead, smell them)
Male
Liquidambar (Capsule)
Flowers
(above)
aka Sweetgum
Female flowers, after pollination, develop into the spikey balls you have probably all seen.
After they dry out and turn brown, the mature seeds are released.
The Sweetgum received its name because the cut bark releases a sweet, fragrant liquid used in some perfumes
Female
Flowers
(below)
Pine (Conifer)
Native Americans used pine tree sap as a way to stop bleeding.
Pine cones are what’s left after the female flower has been pollinated.
Squirrels love to eat them.
Female
Flowers
Male
Flowers
Artichoke (Achene)
The part of the artichoke that we eat
(heart), is a vegetable.
We eat them before the flowers mature.
Typically, the insides or choke (ovaries and eggs), are scooped out and we eat the fleshy support (heart).
It’s in the same family as thistles and the sunflower.
Pineapple (Multiple Fruit of
Berries)
Growers don’t actually want flowers to be pollinated since this would produce seeds.
They make “new” pineapples by twisting off the top stalk and replanting it
(vegetative reporduction!)
Grass (Grain)
Grass plants are 70 to 80% water and clippings are 90% water
The front lawns of 8 average houses have the same cooling effect as 24 (3-4 ton capacity) home central air conditioning units
A 50 by 50 foot grass lawn
(2,500 square feet) releases enough oxygen for a family of four, while absorbing carbon dioxide and other toxins.
Flowers
Dandelion
(Achene - Composite)
The Dandelion provides an important food source to bees.
The pollen from this plant helps bees out in the spring because it flowers early and the flowers continue through to the fall providing constant food.
93 different kinds of insects use
Dandelion pollen as food.
This plant has been used for over
1000 years for medicinal purposes.
Apple (Pome)
Apples are not grown from seed, they are either propagated by grafting or budding (asexual).
Apples are a member of the rose family
It takes the energy from 50 leaves to produce one apple.
Apples are the second most valuable fruit grown in the United
States. Oranges are first.
Orange (Hesperidium)
Navel oranges are named that because of the bellybutton formation opposite the stem end. The bigger the navel in an orange, the sweeter it will be.
After chocolate and vanilla, orange is the world's favorite flavor.
Christopher Columbus brought the first orange seeds and seedlings to the
New World on his second voyage in 1493.
Dogwood (Drupe)
Bark of flowering dogwood was used to treat mange, which may explain the origin of the name.
Extracts and teas from different species were used as a muscle rub, to promote sweating to break a fever, and to treat malaria.
Dogwood was used to treat insomnia.
It was also used for whooping cough and asthma.
Dogwood was an early toothache treatment and it was a
"toothbrush."
The bark, twigs, flowers, berries, leaves and roots are all usable.
Corn (Grain)
An ear of corn averages
800 kernels in 16 rows.
Every piece of corn silk is actually the leftover style and leads to an individual ovary (eventual kernel)
Each year, a single U.S. farmer provides food and fiber for 129 people - 97 in the U.S. and 32 overseas.
Female
Flowers
Male
Flowers
Maple (Samara)
It takes 30-50 gallons of sap to make one gallon of maple syrup
Tapping does no permanent damage to the tree and only 10 percent of the sap is collected each year.
Many maple trees have been tapped for 150 or more years.
The flowers are pollinated by bees.
Birds, squirrels, and other rodents usually consume only a negligible amount of the seeds.
Tomato (Berry)
The botanical family of tomatoes is the same nightshade family as tobacco, potatoes, aubergine
(eggplants), chilli peppers, and the poisonous belladonna.
While the fruit is perfectly safe and healthy to eat, the plant's leaves are actually toxic.
Berry: simple, fleshy fruit that usually has many seeds (e.g., the banana, tomato, or cranberry). The middle and inner layers of the fruit wall often are not distinct from each other
Pumpkin (Pepo)
Pumpkins contain potassium and Vitamin A.
Pumpkin flowers are edible.
In early colonial times, pumpkins were used as an ingredient for the crust of pies, not the filling.
The largest pumpkin ever grown weighed 1,140 pounds.
Pumpkins are 90 percent water.
Male
Flower
Female
Flower
Redwood (Conifer)
One tree can weigh 1.6 million pounds
Can live up to 2000 years!
Can reproduce through seeds or by shoots.
(sexual or asexual)
Redwood trees use their needles to condense fog and let it drip down on their own roots!
Female Flowers appear only on the tips of the uppermost branches
Sunflower
(Achene)
Sunflower heads consist of 1,000 to 2,000 individual flowers joined together by a receptacle base.
The large petals around the edge of a sunflower head are individual ray flowers which do not develop into seed.
A well-known sunflower characteristic is that the flowering heads track the sun's movement, a phenomenon known as heliotropism.
Agapanthus (Capsule)
The pollen is blue.
Bees pollinate the flower.
The perennial Agapantus grow from an underground rhizome each year (asexual)
Agapanthus is suspected of causing haemolytic poisoning (ruptures red blood cells) in humans, and the sap causes severe ulceration of the mouth.
Agapanthus contains several chemicals that have anti-inflammatory (reduce swelling and inflammation), anti-oedema (oedema swelling due to accumulation of fluid), antitussive (relieve or suppress coughing) and immunoregulatory (have influence on the immune system) properties.
Olive (Drupe)
The color of the olives depends on when they were harvested. Green ones are less ripe, black are more ripe.
Olives straight from the tree don’t taste right until they’ve been cured in a salty solution.
No olive trees come from seeds, all are from cuttings of a “parent” tree
(actually a clone!)
The olive produces two kinds of flowers: a perfect flower containing both male and female parts, and a staminate flower with stamens only.
Chinquapin
In the chestnut family edible