6 Functions of Urinary System
advertisement

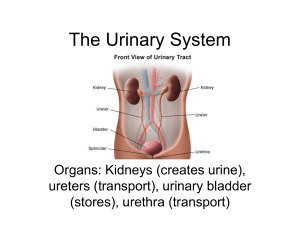
Three major areas of ridding the body of waste (not including digestive wastes) Exhalation CO2 Sweating Toxic metals Elimination Urine Designed to help keep body in homeostasis by removing and restoring selected amounts of solutes and water from blood. 6 Functions of Urinary System Kidneys filter large amts of fluid from bloodstream to eliminate Nitrogenous wastes Drugs, medications and toxins excess water Kidneys maintain blood volume by regulating a balance between salts and water Amt of urine produced Concentration of ions Sodium Chloride Potassium Calcium Phosphate ions Kidneys control balance of hydrogen ions Kidneys produce an enzyme RENIN which helps adjust filtration pressure. Kidneys produce erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates red blood cell production. Kidneys convert vitamin D to calciferol, which enhances the uptake and absorption of calcium and other Kidney – paired organs located under diaphragm; creates urine Ureter – duct from each kidney to bladder Bladder – hollow muscular organ collect urine for excretion Urethra – small tube leading from bladder to outside of body. Transports urine via peristalsis A lesson in Nephrology Renal Capsule – outmost covering of kidney Cortex – outer area extending from capsule to pyramids Medulla - inner area containing pyramids Renal Pyramid – triangular structures inside medulla Papillae – tips of pyramids Nephron – the functional unit of the kidney Medulla is composed of millions of these microscopic collecting tubules. It is here that blood is passed through capillaries and filtered of toxins and excess water & ions 1. Blood vessels 2. Bowman’s capsule From the renal artery, Inside this double- blood enters afferent arterioles leading to Bowman’s Capsule layered globe is the glomerulus, a tiny network of capillaries. This is the site where water and solute filtration happens The filtered fluid flows into the renal tubule 3. Renal Tubule 4. Loop of Henle Nutrients (salts, Tissue around the vitamins, etc.) are moved out of the tubule through active transport. Water follows the nutrients by osmosis. Urine and other solutes continue on Loop of Henle is salty, from active transport and diffusion of sodium chloride. The salty conditions allow water to diffuse out of the loop. 5. Distal tubule 6. Collecting Duct Active transport is More water leaves the used to move more nutrients out of the concentrated urine. Some ions, drugs, and toxins are actively pumped into the tubule tube by osmosis, since the tube is surrounded by salty tissue. Some urea leaves by diffusion, and may be cycled through the system. Urine is a fluid that is composed of about 95% water. It also contains Urea (converted from ammonia) Uric acid Amino acids (few) Electrolytes The average person makes between .6 and 2.5 liters a day! Each collecting tubule leads ultimately through the calyces and to a ureter. The ureter channels urine to the bladder. The urine will then empty from the bladder via the urethra.