kidneys - De Anza College
advertisement

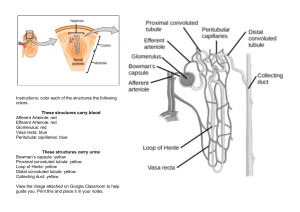
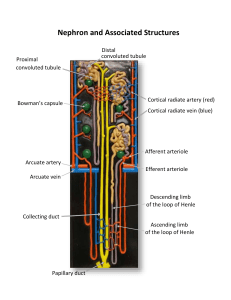
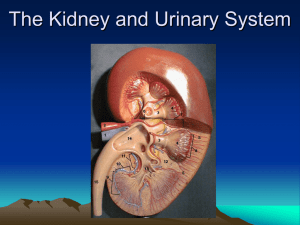
Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS: • Ureters – Collect urine from kidneys, bring to bladder • Bladder – Muscular, elastic organ – holds about 250ml • Urethra – Longer in males than in females – Two sphincters: involuntary & voluntary KIDNEYS • Filter blood, produce urine (24 hrs a day) • Cortex and medulla; At hilus, artery in, vein and ureter out Nephron Structure • Bowman’s capsule & glomerulus – Filtration occurs here – Pressure forces filtrate through cell gaps – Formed elements (blood cells), large proteins stay in blood – Water, ions (salts), nutrients, wastes go through • 180 liters filtrate per day • Proximal convoluted tubule – Majority of reabsorption occurs here. 179 liters reclaimed to peritubular capillary network – Water, salt, glucose, amino acids back to the blood (nutrients in general) • Secretion – removal from blood of wastes that escaped filtration – Loop of Henle ( ascending and descending limbs) – Distal convoluted tubule – Collecting duct Nephron Functions • Filtration: Bowman’s capsule, glomerulus) • Reabsorption: Proximal convoluted tubule • Secretion: Loop of Henle, Distal convoluted tubule , Collecting duct Concentration of Urine • Kidneys regulate water-salt balance of the blood. • Kidney cells use ATP to set it up (pump NaCl & urea leaks into renal medulla) • Descending loop of Henle: water diffuses into salty medulla tissue • Ascending loop of Henle: not water permeable!!!!! Salt is actively pumped out • Distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct: water permeability under hormonal control • ADH (Antidiuretic hormone-secreted by pituitary gland) – Increases urine concentration – When ADH decreases, kidneys make dilute urine – Alcohol interferes with ADH secretion dilute urine, you lose water – coffee too Urine Composition • 95% water by volume; rest is solutes • Nitrogenous wastes: urea, creatinine, uric acid • Ions: sodium, potassium, sulfate, • Associated with medical problems: glucose, blood proteins (albumin), red or white blood cells, bile pigments Renal Failure • Symptoms: – Acidosis – low blood pH - kidneys excrete hydrogen ions – Anemia – low RBC count – erythropoietin – Edema – water and salts retention – Hypertension – high blood pressure – Accumulation of nitrogenous wastes (urea) • Hemodialysis – artificial kidney • Kidney transplant Kidney Stones • Mineral crystals (often calcium) that form in the kidney and pass down ureter. • Prevention: drink plenty of water