Mutations
advertisement

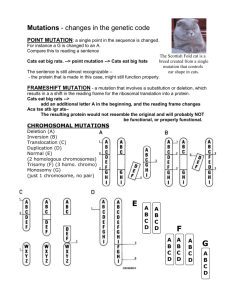
Mutations Mutations Now and then cells make mistakes in copying their own DNA, inserting an incorrect base or even skipping a base as a new strand is put together → these mistakes are called mutations mutation – changes in the genetic material Kinds of Mutations What is a gene mutation? A gene mutation produces a change in a Single gene. What is a chromosomal mutation? A chromosomal mutation produces changes in a whole chromosome. Gene Mutations Two types of gene mutations are point mutations and frameshift mutations. What is a point mutation? A point mutation occurs when there are changes in one or a few nucleotides. They include substitutions, insertions, and deletions. Point Mutation: Substitution Starting Sentence THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT If a substitution occurred…. THE FAT CAR ATE THE RAT Point Mutation: Substitution Substitutions usually affect no more than a single amino acid. Gene Mutations What is a frameshift mutation? A frameshift mutation (usually caused by insertions or deletions) shifts the “reading frame” of the genetic message. These mutations may change every amino acid that follows the point of the mutation Frameshift mutations can alter a protein so much that it is unable to perform its normal functions Frameshift Mutation: Deletion Starting Sentence THE FAT CAT ATE THE RAT If a deletion occurred…. THE FAT CAA TET HER AT Frameshift Mutation: Insertion In an insertion, an extra base is inserted into a base sequence. Chromosomal Mutations The four types of chromosomal mutations are: deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. Chromosomal Mutations Mutation Description deletion Part of the chromosome is lost. duplication Extra copies of part of a chromosome are made. translocation Part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome. inversion Sections of a chromosome are reversed. Deletion Duplication Translocation Inversion Significance of Mutations Most mutations are neutral. What does this mean? They have little or no effect on the Expression of genes or the function of the proteins for which they code. Significance of Mutations What is the significance of mutations to living things? 1. Mutations can be harmful by producing defective proteins that disrupt normal biological activities. 2. Mutations are a source of genetic variability and can be beneficial. Practice 1. Suppose a deletion occurred in the following strand of DNA deleting the first G: A G T C A G G T A How would it change the product of protein synthesis (how would it change the amino acid chain that would be translated from the original DNA strand)? Section Quiz 1. A mutation in which all or part of a chromosome is lost is called a(an) a. duplication. b. deletion. c. inversion. d. point mutation. Section Quiz 2. A mutation that affects every amino acid following an insertion or deletion is called a(an) a. frameshift mutation. b. point mutation. c. chromosomal mutation. d. inversion. Section Quiz 3. A mutation in which a segment of a chromosome is repeated is called a(an) a. deletion. b. inversion. c. duplication. d. point mutation. Section Quiz 4. The type of point mutation that usually affects only a single amino acid is called a. a deletion. b. a frameshift mutation. c. an insertion. d. a substitution. Section Quiz 5. When two different chromosomes exchange some of their material, the mutation is called a(an) a. inversion. b. deletion. c. substitution. d. translocation.