Cell Membrane Practice
advertisement

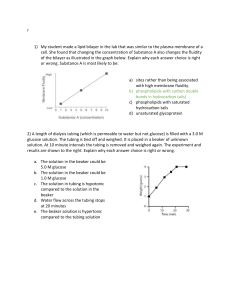
Membrane Test Preparation Define the key characteristics of the following transport terms: 1. Active Transport _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 2. Diffusion _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 3. Facilitated Diffusion _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 4. Osmosis _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Classifying each of the following examples as Active Transport (AT), Diffusion (D), Facilitated Diffusion (FD), and Osmosis (O). Place the letter designation in the blank to the right of each example. Water absorbed by plant roots A drop of food coloring in a beaker of water The smell of a skunk The movement of highly concentrated H+ ions from one side of the membrane to the other side of a membrane through a protein channel Movement of oxygen from the blood stream into the oxygen starved muscle cells. Water rushing out of a cell placed into a hypertonic solution Glucose molecules moving out of a dialysis tubing bag into the beaker of IKI The endocytosis of food particles outside the cell with the expenditure (spending) of ATP Swollen ankle soaked in a salt bath Large molecules moving across a membrane through a transport protein from high concentration to low concentration Sodium ions moving across a membrane against diffusion Define the key characteristics of the following vocabulary terms: 1. Homeostasis _______________________________________________________________ 2. Equilibrium _______________________________________________________________ Classifying each of the following scenarios as an example of Homeostasis (HO) or Equilibrium (EQ). Place the letter designation in the blank to the right of each example. Body temperature stays at 98.6 Body regulates glucose levels in the bloodstream Water moves across both sides of a membrane in equal proportions Guard cells open and close to regulate loss of water by the stomates by transpiration New car smell all throughout the car interior Water rushing out of a cell placed into a hypertonic solution Glucose molecules moving out of a dialysis tubing bag into the beaker of IKI In each of the beakers draw a cell. Place dots in the cell and the solution to illustrate the concentration of each. Draw arrows to indicate which direction the net flow of water would be. HYPOTONIC ISOTONIC HYPERTONIC Circle the celery stalk that is experiencing the greatest turgor pressure. Label the solution (hypertonic or hypotonic) in each beaker. _______________ ______________