Example
advertisement

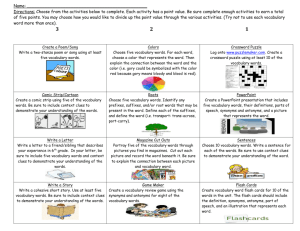
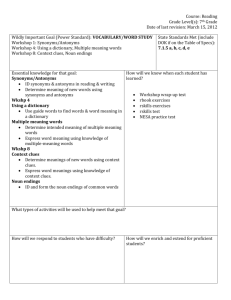
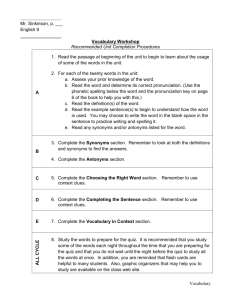
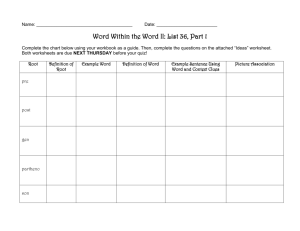
Welcome to Seminar for UNIT 3 Dr. Angela Lavine KU120 The Effective Reader (Updated Edition) by D. J. Henry Chapter 2: Vocabulary Skills REFERENCE: PowerPoint Presentation by Gretchen Starks-Martin St. Cloud State University, MN Key Concepts • The context of the reading is one to deduce the meaning of a word • Improving you vocabulary will increase reading comprehension Unit Outcomes • Identify meanings of unknown vocabulary words using different methods To-Do List • Respond to Discussion Board Question 30 points • Attend synchronous seminar or submit seminar option 2 assignment 5 points • Take Diagnostic Skills Test 50 points Reading • Reading 1 • Read Chapter 2 pages 47–104 • Reading 2 (Online) • Using Vocabulary Words in Reading Key Unit Terms • Antonym - A word that has the opposite meaning of • • • • • • • another word. Context clues - Information that surrounds a new word, and is used to understand its meaning. Glossary - A list of selected terms with their definitions as used in a specific area of study. Prefix - A group of letters with a specific meaning added to the beginning of a word (root) to make a new word. Root - The basic or main part of a word. Prefixes and suffixes are added to roots to make a new word. Suffix - A group of letters with a specific meaning added to the end of a word (root) to make a new word. Synonym - A word that has the same or nearly the same meaning as another word. Vocabulary - All the words used or understood by a person. Vocabulary is all the words used or understood by a person. • • • • By the time you are 18, you know about 60,000 words. During college you learn an additional 20,000 words. Each subject has its own set of words. You can learn new words through: – Context Clues – Word Parts – Visuals Context Clues: The SAGE Approach • A context clue is the information that surrounds a new word, used to understand its meaning. • The four types of context clues are: – Synonyms – Antonyms – General sense of the passage – Examples Synonyms • A synonym is a word that has the same or nearly the same meaning as another word. • Synonym signal words are: or, that is • Example: The dentist gave me laughing gas to alleviate (or ease) the pain of taking out my wisdom teeth. Antonyms • An antonym is a word that has the opposite meaning of another word. • Antonym signal words are: but, not, unlike, in contrast, yet, however. • Example: During dinner, Anne let out a loud burp that mortified her mother, but amused her friends. General Context • Sometimes a definition is provided. • Sometimes a description is provided. • Sometimes logic and reasoning skills are needed. • Example: To insure safety, written and road tests should be mandatory for everyone who seeks a driver’s license for the first time; no exceptions should be allowed. • Jamie speculated about how much weight he wanted to gain during the three-month bodybuilding program he was beginning for the first time. “Speculated” means: – – – – Knew Wondered Worried Celebrated • Jamie speculated about how much weight he wanted to gain during the three-month bodybuilding program he was beginning for the first time. “Speculated” means: – Knew – Wondered – Worried – Celebrated Examples • An example is provided of the word. • Example signal words indicate that an example is coming: for instance, such as, consists of, including • Example: Some authors use pseudonyms; for example, famous American author Mark Twain’s real name was Samuel Clemens. Textbook Skills: Using a Glossary • A glossary is a list of selected terms with their definitions as used in a specific area of study. • Skim the chapter before reading and look for specialized terms (Pre-reading!). • Use the glossary to make vocabulary lists. Word Parts • Root: the basic or main part of a word. • Prefix: A group of letters added to the beginning of a root word to make a word. • Suffix: A group of letters added to the end of a root word to make a word. • Example: in-vis-ible Complete the Practices in your book for an in depth explanation of roots, suffixes, and prefixes and how they can help you understand words. Practice • 1) I took the tome off the shelf and opened it to page 94. Then I began to read. • What does tome probably mean? • A) some food B) a bad dream C) a cigarette D) a book Practice • 1) I took the tome off the shelf and opened it to page 94. Then I began to read. • What does tome probably mean? • A) some food B) a bad dream C) a cigarette D) a book • 2) Hurricanes and tornadoes are treacherous. Only a very foolish person would go out during that kind of weather. • What does treacherous probably mean? • A) exciting B) dangerous C) delirious D) safe • 2) Hurricanes and tornadoes are treacherous. Only a very foolish person would go out during that kind of weather. • What does treacherous probably mean? • A) exciting B) dangerous C) delirious D) safe • 3) Many ships have vanished during hurricanes. No survivors from the lost ships have ever been found. • What does vanished probably mean? • A) arrived B) departed C) returned D) disappeared • 3) Many ships have vanished during hurricanes. No survivors from the lost ships have ever been found. • What does vanished probably mean? • A) arrived B) departed C) returned D) disappeared • 4) By anticipating the robber's next move, the police were able to arrive at the bank before the next robbery happened. Now the robber is in jail. • What does anticipating probably mean? • A) thinking ahead, expecting B) drawing, painting C) horrifying, amazing D) strange, unusual • 4) By anticipating the robber's next move, the police were able to arrive at the bank before the next robbery happened. Now the robber is in jail. • What does anticipating probably mean? • A) thinking ahead, expecting B) drawing, painting C) horrifying, amazing D) strange, unusual • 5) I'm really hungry! That apple didn't appease my hunger. I want a sandwich now. • What does appease probably mean? • A) frustrate B) increase C) satisfy D) confuse • 5) I'm really hungry! That apple didn't appease my hunger. I want a sandwich now. • What does appease probably mean? • A) frustrate B) increase C) satisfy D) confuse • 6) The dispute about marijuana in California will probably never be resolved. • What is a dispute? • A) theory, rule B) argument, debate C) agreement D) a type of medicine • 6) The dispute about marijuana in California will probably never be resolved. • What is a dispute? • A) theory, rule B) argument, debate C) agreement D) a type of medicine Visual Vocabulary • A graph, chart, cartoon, or photograph gives a visual image of a word. Chapter Review • There are four types of context clues (SAGE): – Synonyms – Antonyms – General context – Examples Chapter Review • Antonyms help you see the shade of a word’s • • • meaning by showing you what the original word is not. The root is the basic or main part of a word. The prefix is a group of letters with a specific meaning added to the beginning of a word (root) to make a word. The suffix is a group of letters with a specific meaning added to the end of a word (root) to make a new word.