Acid and Bases
advertisement

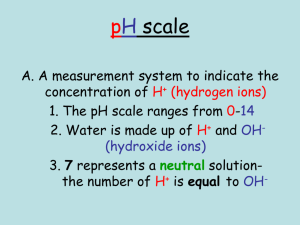
Acid and Bases Physical Properties Acid Taste sour Citric Acid and Ascorbic: lemons Carbonic and Phosphoric: carbonated beverages Acetic Acid: vinegar Conduct electricity Base Taste bitter Feel slippery: wet soap Conduct electricity Chemical Properties • • • • Reactions Litmus paper Red = Acidic Blue = Basic • Reactions • Metals and Metal Carbonates • Produce H2 or CO2 • Geologists identify limestone with hydrochloric acid Videos Links on DHS Chemistry blog Ions Hydrogen Ion H+ Sometimes H3O+ Hydroxide OH- Goes back and forth Hydrogen Bond Notice Exponent on 10 Is opposite of pH pH = - log [H+] Think in terms of the base pOH [OH-] 14 1 x 10-14 pOH = -log [OH-] pH + pOH = 14 7 1 x 10-7 0 1 x 100 Water gains H+ Water loses H+ Neutralization Base + Acid Salt + Water HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) What type of compounds are each? Acid Neutralizers Limestone Calcium carbonate CCaO3 Oceans and Acid Rain Sometimes antacids can interfere with medications Acid Base Reaction then Decomposition Why do some breads have holes? HC2H3O2(aq) + NaHCO3aq) NaC2H3O2(aq) + H2CO3(aq) H2CO3(aq) CO2(g) + H2O(l) Practice Write the balanced equation for the reaction between zinc and nitric acid. Write the balanced equation for the reaction between magnesium carbonate and sulfuric acid. Answers Zn(s) + 2HNO3(aq) Zn(NO3)2(aq) + H2(g) MgCO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) How do you know if you get hydrogen gas or carbon dioxide gas? Practice Identify the base in the reaction. H2O(l) + CH3NH2(aq) OH-(aq) +CH3NH3+(aq) • The base is CH3NH2(aq) • The reactants have an acid and a base • The products have conjugate pairs – match up (think Alg 2) • There is an OH- ion in the products which is the conjugate (or pair) base • What did the OH- start as? This is the acid (opposite of base) • So, the other compound must be the base. Practice Is the solution in which [H+] = 1.0 x 10-5M acidic, basic or neutral? Is the solution in which [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-11M acidic, basic or neutral? Answers Is it H+ or OH-? • H+ so low pH is more acidic, pH = 5, <7 so slightly acidic • OH- so low pOH is basic, pOH = 11, >7 so strong acidic Or, think pH = 14 – pOH so pH = 3, strong acid Practice – Neutralization Write the formula equation for the reactions between hydrioric acid and beryllium hydroxide. Write the formula equation for the reactions between perchloric acid and lithium hydroxide. hydrioric acid and beryllium hydroxide Hyrd = hydrogen =H ioric = iodine = I Covalent bonding, share 1 eBeryllium = Be is group 2 so 2+ Hydroxide = OH- is 1- so need 2 Ionic bonding, metal and ion HI Be(OH)2 perchloric acid and lithium hydroxide Chloric = Chlorine and Oxygen and acid so need Cl and O and H HCIO4 (need a list of common acids) Lithium = Li is group 1 so 1+ hydroxide = OH- so need 1 Ionic bonding, metal and ion LiOH Answers 2HI(aq) + Be(OH)2(aq) BeI(aq) + 2H2O(l) Think how many water? So balance the H HCIO4(aq) + LiOH(aq) LiCIO4(aq) + H2O(l) Keep the ClO4 as a unit even if it does not have ( )