Acids and Bases
advertisement

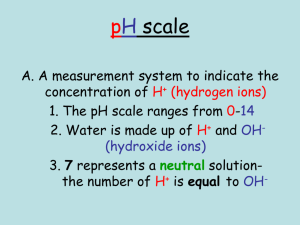
Acids and Bases Acids • Tart or Sour taste • Electrolytes • React with bases to form H2O & a salt • Produces H+ (hydrogen ions) when dissolved in H2O • General form - HX Bases • • • • Bitter Taste Feel slippery Electrolytes React with acids to form H2O & a salt – • Produces OH (hydroxide ions) when dissolved in H2O Naming Acids • Identify name of anion • Anion ends in “-ide”, acid name begins with “hydro” – (Cl - chloride) • Stem of anion ends in “-ic”, followed by “acid” – HCl Hydrochloric Acid – H2S Hydrosulfuric Acid Naming Acids cont. • Anion ends in “-ate” – (SO4 - sulfate) • Stem of the anion ends in “-ic”, followed by “acid” – H2SO4 Sulfuric Acid – HNO3 Nitric Acid Naming Acids cont. • Anion ends in “-ite” – (SO3 - sulfite) • Stem of the anion ends in “-ous”, followed by “acid” – H2SO3 Sulfurous Acid – HNO2 Nitrous Acid Write the Formula • • • • Chloric Acid Hydrobromic Acid Phosphorous Acid Carbonic Acid • • • • HClO3 HBr H3PO3 H2CO3 Naming Bases • Ionic compounds • Name as an ionic compound – Name of cation followed by anion • NaOH Sodium Hydroxide • Ca(OH)2 Calcium Hydroxide Water • Water molecules are highly polar – Continuous motion • Occasionally, collisions between H2O molecules are energetic enough to transfer a H+ -- Self-ionization H2O + H2O H3O+ + OH• H3O+ – Hydronium Ion Water (cont.) • Self-ionization reaction – H2O(l) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) • Pure H2O at 25 °C – [H+] = [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-7M • Ion-product constant for water (Kw) – Kw = [H+] x [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14M2 Acidity + (H )/Basicity (OH ) • Acidic solutions – [H+] is greater than [OH-] – [H+] is greater than 1.0 x 10-7M – [OH-] is less than 1.0 x 10-7M • Basic solutions – [H+] is less than [OH-] – [H+] is less than 1.0 x 10-7M – [OH-] is greater than 1.0 x 10-7M Acidic or Basic Solution? Not all solutions are neutral!!! [H+] = [OH-] • Acidic soln – release H+ • HCl(aq) H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) • Basic Soln – release OH• NaOH(aq) Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) • [H+] > 1.0 x 10-7M • [H+] > [OH-] • [H+] < 1.0 x 10-7M • [H+] < [OH-] Classify – Acidic, Basic, Neutral • [H+] = 1.0 x 10-9M • [OH-] = 2.0 x 10-5M • If [H+] = 1.0 x 10-4M, is the solution acidic, basic or neutral? • What is the [OH-]? • Basic • Basic • Acidic • Kw = [H+] x [OH-] • [OH-] = Kw / [H+] • [OH-] = 1.0 x 10-14M2 / 1.0 x 10-4M • = 1.0 x 10-10M pH Scale • pH – scale used to express [H+] • Ranges from 0 – 14 – pH=0 Strongly acidic – pH=14 Strongly basic • pH = - log [H+] Ex. Neutral Solution [H+] = 1.0 x 10-7M pH = - log (1.0 x 10-7M) = 7 pH cont. • [H+] > 1.0 x 10-7M – then pH < 7 (acidic) • [H+] < 1.0 x 10-7M – then pH > 7 (basic) • Recall [H+][OH-]= 1.0 x 10-14M • Calculations: • [H+] = 6.0 x 10 -10M Acidic or Basic? pH = ? [OH-] = ? pOH Scale & calculations • pOH– scale used to express [OH-] • pOH = - log [OH-] • pH + pOH = 14 • If pH = 6.5, calculate pOH & [OH-]. • pOH = 14 – 6.5 = 7.5 • [OH-]= 10-pOH = 10-7.5 = 3.1 x 10-8M Measuring pH • Why – swimming pools, soil, medical (diabetes) • How – 1. Acid – Base indicators – change color at a specific pH • Ex. phenothalein, thymol blue … – (Pg. 590 Figure 20.8) – 2. Litmus paper – 3. pH meters – make rapid & accurate measurements Assignment Name each acid or base: • a. HF • e. HClO3 b. KOH f. Al(OH)3 c. HNO3 g. H3PO3 d. H2SO4 h. Fe(OH)3 Write the formula for each acid or base: • • • • a. barium hydroxide c. chromic acid e. rubidium hydroxide g. chlorous acid b. hydroselenic acid d. hydrobromic acid f. iron(II) hydroxide h. sulfurous acid Identify each property as applying to an acid, a base or both. • a. bitter taste • c. electrolyte b. indicator color change d. sour taste Assignment Continued • Pg. 658 – 35, 41-43 • pH Worksheet