PowerPoint- How are acids and bases different?
advertisement

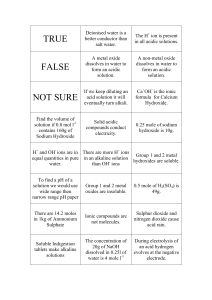
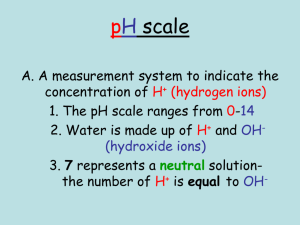
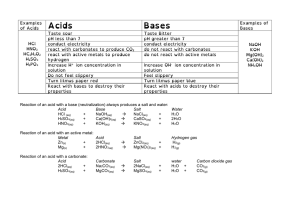
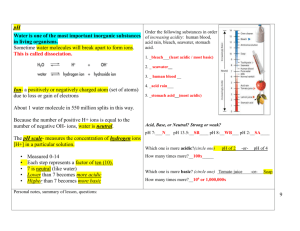
Date: October 19, 2015 Aim #17: How are acids and bases different? Do Now: Warm-Up Notebook Date 10/19 Title of Activity Properties of Water Page # 32 HW: 1)Worksheet- Properties of Water Due Tuesday 2)Guided Reading 2-2 Due Thursday 3)Quiz (Inorganic Chemistry)- Wednesday 10/21 & Thursday 10/22 (day of double period) Aim #17- How are acids and bases different? What does the pH scale measure? • Measures the hydrogen ion (H+) concentration of a solution. Acid pH 0-6 Neutral pH 7 Base pH 8-14 What is an acidic solution? • Any compound that produces H+ ions in solution • Consists of molecules that contain H covalently bonded to another group of atoms • When this molecule is put in water, it will dissolve and the H breaks loose as an H+ Example: HCl (hydrochloric acid) • HCl without water is a gas, but when dissolved in water the H becomes an H+ and Cl becomes a Cl- What is a basic solution? • Any compound that produces hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water • Example: NaOH (Sodium Hydroxide) • separates when dissolved in water, the Na becomes Na+ and the OH becomes OH- What is a neutral solution? • A solution with a pH of 7 • Contains equal concentrations of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-) • Example: pure water *distilled water is considered to be pure water Concept Check: Let’s Review Acids and Bases by completing the chart below! ACIDS BASES H+ concentratio n (high/low) High Low pH value Lower than 7 Higher than 7 Examples Acid rain, vinegar, Seawater, blood, lemons bleach Neutral Equal concentrations of H+ and OH- 7 Distilled water What is neutralization? • When an acid and base are mixed, the H+ from the acid combines with the OH- from the base • The positive and negative cancels each other out and the substance becomes neutral • What happens when H+ and OH- join? • water is formed (H2O)!! How do buffers work? • A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base, thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. • Buffers are found in our body to help neutralize the blood if excess H+ (hydrogen ions) or OH- (hydroxide ions) are present • Acidosis: pH drops too low and blood is too acidic • Alkalosis: pH is too high • Common buffers: HCO3(bicarbonate ion) and H2CO3 (carbonic acid) How can we measure the pH of a solution using indicators? • An indicator is a substance that changes color when pH goes above or below a certain value • Used to see if something is acidic, basic or neutral • Litmus paper: red, blue or white • pH paper • Phenolphthalein: changes from colorless to pink in a moderately basic solution (pH above 10) BrainPop • http://www.brainpop.com/scien ce/matterandchemistry/phscale/ • http://www.brainpop.com/scien ce/matterandchemistry/acidsan dbases/ In Closure….let’s bring it all together! As the concentration of H+ increases, the solution becomes more acidic, and the pH decreases. As the concentration of H+ decreases, the solution becomes more basic, and the pH increases.