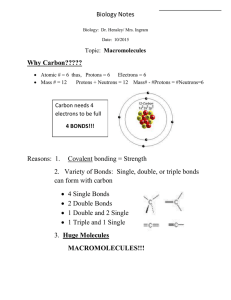
bonds
advertisement
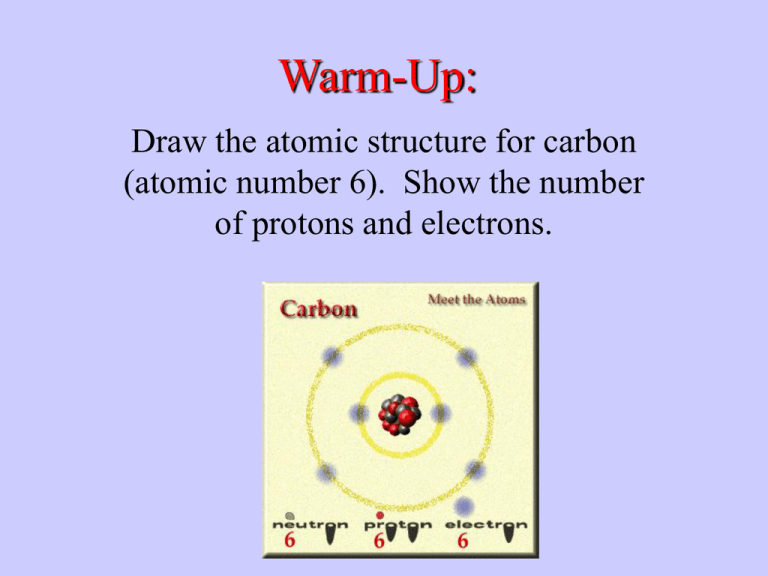
Warm-Up: Draw the atomic structure for carbon (atomic number 6). Show the number of protons and electrons. Chemical Compounds in Living Organisms Two Categories of Compounds: ORGANIC Contain C-H bonding Simplest, Methane CH4 INORGANIC Lack C-H bonding Carbons Bonding Properties Four single covalent bonds Single, Double, or Triple bonds to itself Form long chains, w/ combo of bonds (s, d, t) Form rings, w/ combo of bonds (s,d,t) Easily bonds N,H,O,P, and S 96.3% Total Weight of Human is NCHOPS Nitrogen Hydrogen Carbon Oxygen Phosphorus Sulfur Polymerization Chemical process by which carbon-based compounds are built Small compounds called monomers Monomers joined by bonds to create polymers Extra large polymers are called macromolecules Macromolecules are built inside cells Four Organic Macromolecules I. Carbohydrates II. Lipids III. Proteins IV. Nucleic Acids Composition of a Bacterial Cell I. Carbohydrates Structural Formula for Glucose a. Composed of ONLY C, H, and O b. Two H for every O, 2:1 ratio c. Monomer unit = monosaccharide d. Two monomers = disaccharide e. Three monomers + = polysaccharide A. Monosaccharides Basic formula (CH2O) 2:1 ratio Simplest carbs known as sugars Examples, 5-C sugars ribose and deoxyribose Examples, 6-C sugars glucose, galactose, and fructose - these are isomers, same chemical formula(C6H12O6) different structural formula Glucose made by green plants Galactose found in milk Fructose found in fruits Hexoses: D-Glucose(A), D-Galactose(B), D-Manose(C), DFructose(D) I S O M E R S B. Disaccharides Chemical Formula: C12H22O11 Known as a “double sugar” Two monomers bonded together by dehydration synthesis (anabolic process) A molecule of water is removed; a hydrogen atom from one monomer and hydroxyl group from another Examples: Glucose + Fructose = Sucrose + water (table sugar) Glucose + Glucose = Maltose + water (malt sugar) Glucose + Galactose = Lactose + water (milk sugar) EACH TIME A MONOSACCHARIDE IS JOINED WITH ANOTHER, ONE MOLECULE OF WATER IS REMOVED!!!!! C. Polysaccharides • Large polymers made of sugar monomers • Form in which living organisms store excess sugar • Also used as a structural component • Two Types: 1. Storage Polysaccharides • Starch - plants store sugar as starch - composed of glucose monomers • Glycogen - animals store sugar as glycogen in liver and muscles - also composed solely of glucose 2. Structural Polysaccharides a. Cellulose: - most abundant organic compound on Earth - found only in plants - composed of glucose - most animals cannot digest; fiber in diet; pass out; regulates digestive processes b. Chitin - found in exoskeleton of animals - also found in fungi II. Function of Carbohydrates • Quick energy from sugars • Longer energy storage in polysaccharides • Structural support from polysaccharides III. Getting the Energy • Break apart polymers • Hydrolysis reaction - catabolic reaction that consumes a molecule of water - bond between monomers split - energy released when bonds broken - occurs during digestion of food • Sucrose + Water Glucose + Fructose