Why Carbon????? Biology Notes Macromolecules
advertisement

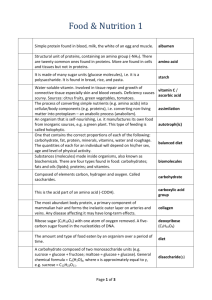
Biology Notes Biology: Dr. Hensley/ Mrs. Ingram Date: 10/2015 Topic: Macromolecules Why Carbon????? Atomic # = 6 thus, Protons = 6 Electrons = 6 Mass # = 12 Protons + Neutrons = 12 Mass# - #Protons = #Neutrons=6 Carbon needs 4 electrons to be full 4 BONDS!!! Reasons: 1. Covalent bonding = Strength 2. Variety of Bonds: Single, double, or triple bonds can form with carbon 4 Single Bonds 2 Double Bonds 1 Double and 2 Single 1 Triple and 1 Single 3. Huge Molecules MACROMOLECULES!!! Making a Polymer out of lots of Monomers: Dehydration synthesis To bond the monomers together the reaction removes H2O Breaking down of Polymer into its Monomers: Hydrolysis Needs H2O to put back into the reaction to break apart the CARBOHYDRATES Monosaccharides = One Sugar The ending “OSE” stands for sugar o Glucose C6H12O6 o Galactose C6H12O6 o Fructose C6H12O6 (Fruit Sugar) Disaccharides = Two Sugars o Sucrose C12H22O11 (Table Sugar) = Glucose + Glucose o Lactose (Milk Sugar) = Glucose + Galactose Polysaccharides = Many Sugars o Starch o Cellulose (Plants for structure) o Chitin (Animals) LIPIDS = FATS o Glycerol o Saturated Fats = Full of Hydrogen Bonds , Have long straight fatty acid chains that can stick closely together to form a solid at room temperature: Butter, Lard, Margarine Glycerol Fatty Acid Side Chains o Unsaturated Fats = Not full of Hydrogen Bonds, Have bent fatty acid chains that do not stick closely together and are liquid at room temperature: Veg. Oils PROTEINS Everything in your body depends on Proteins!!!! AMINO GROUP ACID GROUP “R” Group Determines the kind of Amino Acid 20 Different Amino Acids Nucleic Acids C, H, O, N, P Nucleotides are the monomer of Nucleic Acids Sugar + Nitrogen Base + Phosphate Group DNA, RNA, ATP Structure looks like this: