CARBOXYLIC ACIDS O ||
advertisement

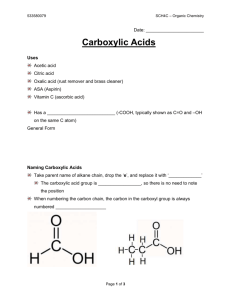
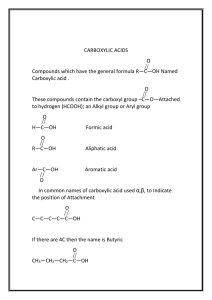
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS O || The functional group in organic acids is the CARBOXYL group: —C—OH The condensed structural formula is –COOH. THE NAMING OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS The IUPAC names of CARBOXYLIC ACIDS are obtained by selecting the longest carbon chain containing the CARBOXYL group and replace the ending of the alkane name with the ending “oic acid”. If an alkyl group is present, the numbering starts from the carbon of the carboxyl group. EXAMPLE: O || CH3 – CH2 – CH – CH2 – CH2 – C - OH | CH2 - CH3 4-ethylhexanoic acid EXERCISE: 1. Name thew following carboxylic acids using IUPAC system: a) CH3 O | || CH3 – CH2 – C – CH2 – C – OH b) CH3 CH3 | | CH3 – CH – CH - COOH | CH3 2. Draw the condensed formula for: a) Heptanoic acid b) 4-methylhexanoic acid PROPERTIES OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS 1. Carboxylic acids have strong odours. 2. Carboxylic acids are capable of HYDROGEN BONDING because they contain a HYDROXYL group. This results in high melting points and high boiling points in these compounds. Since HYDROGEN BONDING is the major intermolecular force, we would expect organic acids with short carbon chains to be miscible with water. 3. Carboxylic acids are weak acids that will dissociate in water to form hydronium ion and a carboxylate ion: EXAMPLE: CH3-COOH ethanoic acid + H20 --> water CH3COO1- + ethanoate ion H3O1+ hydronium ion 4. In the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, carboxylic acids react with alcohols to produce esters. The reaction is called an ESTERIFICATION reaction. methanoic acid + ethanol ethyl methanoate QUESTIONS 1. What ions form when propanoic acid reacts with water? 2. Why does butanoic acid have a higher BP than 3-pentanone? 3. If ethanoic acid is reduced with H2, what two possible products can form? (name and draw their condensed structural formulas) 4. What alcohol needs to be oxidized to prepare 3-methylpentanoic acid?