Unit 3 Notes Part 1 - Aspen View Academy
advertisement

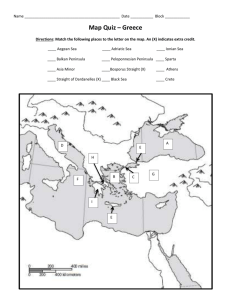
AVA Heading: Unit 3: Ancient Greece Directions: Please fill out the following notes and warm-ups during class. At the end of the unit, during your test, your teacher will grade this packet. If you have any questions filling out this packet, please ask your teacher when appropriate. Thank you! Day 1: Ancient Greece Geography Warm-up: 1. Do all countries have the same form of government? 2. Explain what you know about the American government. 3. Are individuals represented by our government? 4. How do you think you did on the test? 5. How much time did you spend studying? Objectives: Students will be able to identify how different forms of government relate to their citizens. SS 6.4.2.b Ancient Greece: City-State: Greece Geography: Greece is a ___________________. Surrounded on _____ sides by __________. Many __________ ____________. Greece is covered with _________________. Mediterranean Sea: Do Now: (You can use your notes) What is a peninsula? What were the advantages of living on peninsula? Vocabulary: City-State: Colonies: 1 Peninsula: Polis: City-States & Democracy: Not _____________ because of geography. Spoke the same ________________. Worshipped the same ________. Each city-state ruled _____________. Highest Peak: Do now: (You can use your notes) Why were the Greek city-states not united? It is said the Greece is “rugged” land. How does this relate to the land not being fertile? Animals: Raised Sheep: Goats: Sea Provided: Food & easier travel Sailing vessel a trireme - - - - Greece Traded: - Grapes- wine - Pottery - - - - Works of Art - Wool Summary: 1. Why was it difficult for Ancient Greeks to farm? 2. Name the products the Greeks traded? 3. Why did the Greeks become great sailors? 2 Day 2: Introduction to Sparta Warm-up: 1. Why did the Greeks become great sailors? 2. Why wasn’t there communication between city-states? 3. What types of foods were grown? 4. What animals were raised for food and clothing? 5. What else did one of these animals provide? Objectives: Students will be able to identify how different forms of government relate to their citizens. SS 6.4.2.b Greek City-States: The Greeks began to build _________-___________ instead of one _____________. A city-state is a city with its own __________, ____________, and ____________. City-States were _________ that acted like _______________. Sparta: Sparta’s Classes: There were ___________ classes of people in Sparta. ___________, ___________________, and ____________. Only men born in ____________ were ____________. Women were not allowed to become _____________. -Women were allowed to own _________ and ________________. - Women had more ______________ than other Greek city-states. - The _________________ class in Sparta came from other _________-states or other _______________. They could own _________________ but not become citizens. The ______________ class was _____________. Spartan Warriors: Training to become a good ________________ was important. Young ________ were taken from their _______________. Trained to be ______________. They were good at sports such as _______________. Girls were also ________________ to be good in sports. 3 Summary: 1. List the types of classes that existed in Sparta? 2. Who was able to receive an education and who was not able to receive an education? 3. What is a city-state? Map: Label the letters below in your map key. http://staff.harrisonburg.k12.va.us/~cwalton/Mapquizgreece.htm Map Key: A. F. 1. B. G. 2. C. H. 3. D. I. E. J. 4 Day 3: Warm-up: 1. What is the definition of a city-state? 2. Explain who the Spartans were. 3. Were women treated different in Sparta? Objectives: Students will be able to identify how different forms of government relate to their citizens. SS 6.4.2.b Athens: Important __________ city-state. Wanted to rule themselves and not have a _________ or __________. World’s first ___________________ around 508 B.C. A democracy is a government in which all the ___________ can vote and have equal say in what _____________. Democracy in Athens: Pericles: Pericles was the ____________ creating democracy in Athens. He had many buildings ________________. Pericles had the ________________ and the _______________ built. Education in Athens: The Greek Alphabet: The Greeks borrowed their _______________ from the Phoenicians. Most European languages _____________ ideas from the Greek alphabet. Including ______________. Socrates: Socrates was a _________________ of Ancient Greece. A Philosopher is someone who tries to ________________ the nature of ___________. Socrates taught by asking questions. This method of questioning is still called the _______________ method. Plato: 5 Aristotle: Aristotle was another Greek __________________ and student of Plato. He wrote about ____________, art, law, poetry, and ___________________. Summary: 1. What is Athenian Democracy? 2. Who the 3 philosophers of Greece? 3. How did they differ from each other? 4. Who was Alexander the Great? Day 4: Corinth Warm-up: 1. What are 2 similarities between Sparta and Athens? 2. What are 2 differences between Sparta and Athens? Objectives: Students will learn about the city-state of Corinth. Government: Monarchy- rules by a ___________. King had ________________. Solved ___________________ problems by public works programs and building ________________. Education: Boys educated in fine arts & the sciences. Until age 7, a child is educated at home. From 7-14, boys attend a nearby school. Study: poetry, drama, _____________ speaking. Accounting, reading, writing, math, science. Boys attended at least 2 years of military school. 6 Summarize the Story about the King in 4 or more sentences. Summary: Pick one of the three Greek City-States you have learned about and write a paragraph (5-7 sentences) explaining why you would want to live there. 7 Day 5: Democracy in Ancient Greece Warm-up: 1. What is the definition of a polis? 2. What is the geography like in Greece? 3. Using your knowledge, what is the definition of democracy? 4. Why is a democracy important? Objectives: SWBAT identify how democracy in Ancient Greece related to their citizens. SS6.4.2.b SWBAT compare various gov’ts in Greek city-states and the freedoms of their citizens. SS 6.4.2.d Democracy: Demos = Cracy/ - Aids in ______________ problems. Most city-states _________________ Athens. Most voters were __________, free, and owned land. Representative Vote: Most _________________ men did not have time to vote. Leads to a few ____________ men did voting. Chosen by lottery. Served __________ year. Pericles: Famous Greek ________________. All ___________________ had to take part in government. One man, one __________. Who was not allowed to vote? Success of Thebes: o Thebes: Ended _____________ power in 371 BC. Leuctra in 371 BC. Sacred Band of ____________. Elite military force. Fell to Philip II & _______________ the Great. Summary/Discussion: 1. You have now learned about four city-states and how they are governed (type of gov’t). 2. Discussion question is: What city-state would you have lived in and why you would live there? 8 3. Which city-state is left out of the picture? Launch: Is democracy important to you? Day 6: Four Types of Government Warm-up: 1. What are the three things you are supposed to do when entering Mr. Yanaitis’ classroom? 2. What do you do when you hear the emergency alarm? 3. What is democracy? Objectives: SWBAT identify tyranny, aristocracy, oligarchy, and democracy as early forms of Greek government. SS 6.4.2.b Suffix-archy: Meaning “_____________________” Examples: _______________ and ______________. Suffix-cracy: Meaning “______ ___________” or “_______________” Examples: ________________ and ________________. Monarchy: ____________ is in the ____________ of a _____________ person. In power for ________. Mycenaean's created to rule their _____________ Origin o Monos “____________” o Arkhein “____________” Lifestyle of a Monarch: o o Oligarchy: ___________ is in the hands of a ________ people. ______________ Inherited ___________ ___________ oligos “_________” arkhein “___________” 9 Lifestyle of the Oligarchy: Tyranny: ______________ in hands of _________ person. Often _____________ takes control o Origin Tyrannos “____________ power or usurper” Tyrant – ________________, cruel, & ____________ Lifestyle of Tyrant: Reforms in favor of citizens Last important tyrant Hippias of Athens Democracy: ____________ in the hands of _________ people. ________ B.C.E. city-states of ________. Origins o Demos “_____________” o Kratos “______________” Lifestyles of Citizens: Opposed rule of ____________. Citizens of _____________. o Met _____ times a year _____________ Body (Council of 500) o Responsible for day-to-day o Summary: 1. Name the 4 types of Government. 10 2. Which form of government is your favorite and why? Launch: What would the world be without the Democratic USA? Day 7: 4 Forms of Government Activity Warm-up: 1. What government is ruled by the people? 2. What government is ruled by a king or queen? 3. What government is in the hands of a few people? 4. What government is in the hands of one person often illegally? Objective: SWBAT identify tyranny, aristocracy, oligarchy, and democracy as early forms of Greek government. SS 6.4.2.b Group Activity: 1. Read aloud the 4 forms of government. 2. Then fill-out graphic organizer on development of democracy. 3. Divide students into 4 groups 4. Groups will read “political issue” 5. Students will then prepare to debate their counter parts about why their form of government is best. Day 8: Persian Wars Warm-up: 1. Did you enjoy the debate yesterday? 2. Do you have any questions about the debate? 3. What is one thing you learned from yesterday? Objective: 1. Describe the Persian Wars and the battles of Marathon, Thermopylae, Salamis, & Plataea. SS 7.1.1.b 2. Understand the achievements of Sparta and Athens during the wars. SS 7.1.1.b 3. Discuss the leadership during the war. SS 7.1.1.b Battle of Marathon: September 490 ____.____. - 600 _____________ ships - 20,000 _____________ & _____________ - Lead by King ________________ - The ______________ wanted revenge for ______________ from the Greeks during the Ionia ____________.. o Marathon by attacking 1st 11 o Historian __________________ o Trivia: ______________________: Ran from ____________ to ____________ asking for _______________. Then collapsed and _____________ after running from Marathon to Athens to announce ______________. Battle of Thermopylae: Strategy: o Spartan King Leonidas fights for 2 days o Xerxes: Persian ___________ lead by Xerxes. - ________________ men (_____________ immortals) - _________ to __________ ships Sacked and burned ________________ to the ground. Battle of Salamis: This is where _________________ fled to. Xerxes plans ___________ attack. Fighting occurred in the _____________. In the picture, Xerxes looks on with ___________________. Athenian Themistocles Strategy: Prevent Persian navy from aiding ______________ troops. Ships ______ a line across the ______________. Speedy triremes ram Persian ships. _____________ ships and kill crew. Destroyed Persian __________. Battle at Plataea: 12 Summary: 1. List the Persian battles fought and the winner. 2. How did the Ionia Revolt start the Persian Wars? 3. How many land battles were there? 4. How did the battle of Thermopylae end? Day 9: Peloponnesian War Warm-up: 1. Why was it important that the Greeks win the Battle of Marathon? 2. How did the Persians defeat the Greek army at Thermopylae? 3. Who was the historian that wrote about the Persian Wars? 4. Who do you think is going to win the Peloponnesian War: Athens or Sparta? Objective: SWBAT understand how the Peloponnesian War started. SS 7.1.1.b SWBAT describe the battle strategies Athens and Sparta used. SS 7.11.b Peloponnesian War _________ -_________ B.C. Delian League: Based on the island of _____________. Formed to defend against the ______________. Athens gains ______________. Sparta refuses to ____________. Pericles: Sparta and Allies: Feared _______________ increased power. Creates the ______________________ league. Not tolerate of way of life. Strategy: Both _________________ felt they could ___________. Sparta has great land _______________. Athens has a great ______________. 13 Archidamian War Retreat: Citizens of ____________ remained Athenians ________________ by navy, raids on Peloponnesian coast. Invasion of Sicily: 2nd ______________ of attacks in 415 B.C. Source of supply to support war. ______________: Athenians killed or sold into _______________. Aegospotami: On the _________________. Athenian fleet _________________. Athens surrender in _________ B.C. Summary: 1. Who fought in the Peloponnesian War? 2. What was the result of the Peloponnesian War? Day 10: Alexander the Great Warm-up: 1. Who was the leader in Athens during the Peloponnesian War? 2. What was the cause of the Peloponnesian War? 3. Would you be a Spartan or an Athenian? Why? Objective: Understand the accomplishments and victories of Alexander the Great SS7.2.1.b. Recognize the significance of Hellenistic Period SS 6.1.1.a Early Years: Succeeded Philip _____ of Macedon who was his ____________. Olympias of ____________, his _______________. _______________ by famed philosopher __________________. Greek Polis: o o 14 Alexander: __________________ to rule at a _______________ age. By age _________ he was leading his own ______________. At 18, led _________________ against ________________ city-states. o Puts down revolts in Greece o o Captures Thebes and burns it to the ground Persian Invasion: Estimated ____________ - Alexander was a master of the __________________ charge Conquests of Alexander: ______________, Persia, ____________, Afghanistan, ______________, the Middle East, _____________, and part of India. Troops followed him _______________. Troops were ______________ in battle and unafraid. These conquests brought ______________ culture all over the known world. Spread of the Hellenistic Period: Kings made ____________ like Greek coins. Imitated Greek ________________, ________________, philosophy, and science. Built a _________________ in Egypt. Death of Alexander: __________ B.C. falls ill in Babylon. Dies at the age of ______. Generals fought _______________ empire into ______ parts. - (Antigonous) - (Seleucus) - (Ptolemy) Summary: 1. What topic was the most interesting so far in Unit 3? 15 Day 11: Architecture Warm-up: 1. List as many differences between Athens and Sparta as you can. 2. List the four types of gov’t and what they mean? 3. What cause and effect did the mountains have on Greece? Objective: SWBAT understand the influence of architecture on Greece and the world. SS 6.4.1.b SS 6.4.1.c Columns: Columns are part of _________ and ______________ type construction. Egyptians used __________ and ___________ architecture in their _____________. Influence on the Egyptians: The Greeks _______________ post and lintel from the ________________ modifying and developing their own _____________ of column or order decoration. There are ____________ types of Greek columns—which are still used ________________. 1. Doric: The ____________ of Greek order (the _______________) 2. Ionic: The _______________ Greek order (the ______________) 3. Corinthian: The ______________ type of Greek order. Columns are the ___________ important part in ________________. Many Greek buildings are ____________ standing today. Acropolis: Main temple complex in _______________--and Greece. Build by ________________; “________________ age of Athens” Parthenon: Athena’s Temple at the Acropolis. Athena Nike: Goddess of victory in ________ and _____________. Origins of _____________ “________________” 16