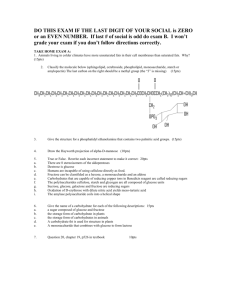
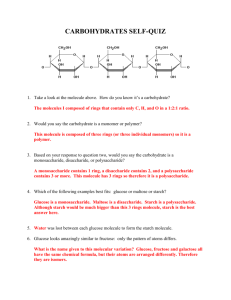
Name(s): Carbohydrates The first step in understanding
advertisement

Name(s):_____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Carbohydrates The first step in understanding carbohydrates is to recognize their structure. Below is the common building block for many carbohydrates. It is called glucose. Glucose can be found in a chain form or the ring form. We will focus on the ring form because that is the form glucose takes in your bodies Step 1: Use the diagram above and molecule packet #1 to build glucose. In the molecule packet you will find the following: White or Green tubes (48) these represent to covalent bond formed between two atoms. Black model pieces (12) these represent carbon atoms. White model pieces (24) these represent hydrogen atoms. Red model pieces (12) these represent oxygen atoms. Follow the diagram above as you join carbon atoms, hydrogen atoms, and oxygen atoms to build your own glucose molecule. Question 1. What functional groups do you see? 2. What property does this functional group give glucose? What will happen to it in water? 3. What is the chemical formula for glucose? 4. What type of carbohydrate is glucose? Circle One: Monosaccharide 5. What is the primary function of glucose? Disaccharide Polysaccharide Step 2: Use the diagram above and the remaining model pieces in packet #1 to build fructose. Note: not all the carbons are shown in the diagram – they are understood to be at the points of the ring. 6. What is the chemical formula for fructose? 7. Do you notice anything about glucose and fructose? What kind of molecules are they? Step 3: Following the diagram above, join glucose and fructose to form sucrose. 8. What type of reaction is this? 9. What two molecules are produced from this reaction? 10. What type of carbohydrate is sucrose? Circle One: Monosaccharide Disaccharide Polysaccharide 11. What is the chemical formula for sucrose? 12. What is the chemical formula for lactose? 13. What kind of molecules are sucrose and lactose (based on their chemical formulas)? 14. Glycogen is polysaccharide found in animals. What are two common polysaccharides found in plants? 15. What are the two functions of polysaccharides?