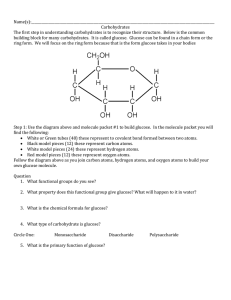
Analysis of Sugar Molecules Name: _________________________________________________ Date: ______________ Introduction: An important group of biological compounds are the saccharides (sugars of carbohydrates). Carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. The many different types of sugars have been grouped into two main categories: Monosaccharides and Disaccharides A. Simple Sugars (a.k.a. monosaccharides) H H C H O \ I H O \ I C H H H H C H H C C C H O \ C I H H O \ I C O \ I H C H C O \ I H O \ I H O \ I O \ I O \ I H C O O \\ II H H H C O \ I H H Glucose H H Fructose QUESTIONS: 1. Fill out the chart below to compare the two molecules. Comparison Name Central Shape Glucose Fructose # of Carbons # of Hydrogens # of Oxygens 2. What is the chemical formula for glucose? C____H____O____ 3. What is the chemical formula for fructose? C____H____O____ 4. What is the ratio of Hydrogen atoms to Oxygen atoms in glucose? _________________ 5. What is the ratio of Hydrogen atoms to Oxygen atoms in fructose? _________________ 6. How does the ratio of Hydrogen atoms to Oxygen atoms in glucose compare to the ratio of H:O in water? B. Disaccharides (“Two sugars”): Disaccharides are formed when two monosaccharides bond together The type of reaction that bonds the sugars together is called dehydration synthesis. The following diagram shows two molecules of glucose bonding together to become a disaccharide through the process of dehydration synthesis: H H H H O \ I C H H O \ I C H H H H H H O \ I C O \ I H Glucose H H + C O \ C I O \ I C C O \ I O \ I C H C H H O \ I C O \ C I H H C O \ I H H O \ I Glucose H H Carefully study the diagram above and notice that an O-H of the glucose on the left is circled and that an H is circled on the glucose on the right. That O-H and H are removed and the molecules join together at that site. When the two molecules are joined together they are called Maltose which is s a disaccharide: H H H H C H O \ I C H O \ I C H H H H H H H H C O \ C I O \ I C C O \ I O \ I C O \ I H H H Maltose C O \ C I C O \ I H H H O \ I C O \ I H H QUESTIONS: Maltose is a sugar not naturally found in high quantities in the food supply, but your body can generate it when you digest starchy foods. It is an important component in brewing beer and distilling alcohol, and provides a distinct flavor to malted beverages. 1. What is the chemical formula for maltose? C____H____O____ 2. How does the ratio of H:O atoms in maltose compare to the H:O ratio in glucose and in H2O? 3. Why do you think this reaction is called a dehydration synthesis? (Hint – look at the atoms that came off of the sugars.) The following diagram shows molecule of glucose bonding together with a molecule of fructose to become a disaccharide through the process of dehydration synthesis: H H C H O \ I H O \ I C H H C H H H O \ I C H O \ I Glucose C H C H O H \ I H C O \ I H HH C O \ I H H H O \ I O \ I O \ I C + C O \ C I H H C O \ I H H H H Fructose Carefully study the diagram above and notice that an O-H of the glucose on the left is circled and that an H is circled on the fructose on the right. That O-H and H are removed and the molecules join together at that site. When the two molecules are joined together they are called Sucrose which is s a disaccharide. H H C H O \ I H O \ I C H H C H C H H O \ I H H H C C O \ I C C O \ I H H O \ I O \ I O \ I C C O \ C I H H H O \ I H H H H C O \ I H Sucrose QUESTIONS: Sucrose is a common sugar found in many plants. It is ordinary table sugar. 4. What is the chemical formula for sucrose? C____H____O____ 5. How does the ratio of H:O atoms in sucrose compare to the H:O ratio in maltose and in H2O?