Label the following bonds as polar and nonpolar.
advertisement

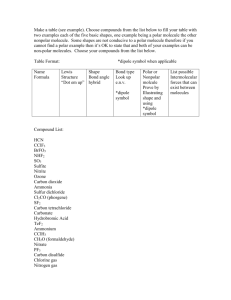
Warm Up: Octet Rule a filled layer contains 8 electrons Exceptions (After bonding…) H and He will have 2 Beryllium will have 4 Boron will have 6 Some transition metals can have more than 8 Dot Diagrams for Molecules Atom with most unshared electrons goes in middle *capable of forming most bonds* Count to make sure you have the right number of electrons Each atom wants to have a full valence Try these… CH4 O2 CO2 NH3 N2 H2O Domains Write the shapes of each of the dot diagrams you made before Warm Up: Label the following bonds as polar and nonpolar. Br2 HCl H2 CH4 NH3 Molecular Polarity Dipole Molecule with an overall unequal distribution of electrons Two atom molecules If the bond is non-polar, so is the molecule If the bond is polar, the molecule has a dipole and is polar Do these molecules have dipoles? N2 O2 CO HF Three atom molecules If the 2 polar effects are equal and oppositely directed, the molecule is nonpolar Otherwise, the molecule is polar Carbon dioxide water Four atom molecules It is possible that the 3 polar effects may cancel and produce a nonpolar molecule It is also possible that they don’t cancel and produce a polar molecule Exception to octet rule NH3 (ammonia) Five atom molecules It is possible that the 4 polar effects may cancel and produce a nonpolar molecule It is also possible that they don’t cancel and produce a polar molecule CH4 CH3Cl Intermolecular Forces Between molecules Dipole-dipole Hydrogen bonding Van der Waals Dipole-Dipole Like electrical charges and magnets, dipoles can attract one another Stronger attractions with stronger dipoles Stronger attractions when molecules are closer together with lower temperature and higher pressure Hydrogen Bonding Occurs when Hydrogen and Fluorine, Oxygen, or Nitrogen are present FON Ammonia, hydroflouric acid, water Higher boiling points with hydrogen bonding Van der waals Recall that electrons have a little bit of freedom to move around their electron clouds VDW are produced by momentary uneven electron distributions Extremely weak Responsible for bonding of nonpolar molecules, liquefaction of inert gases, 3 phases of halogens at STP Stronger for molecules with more electrons Gets stronger as molecules get closer bromine