Lecture 10
advertisement

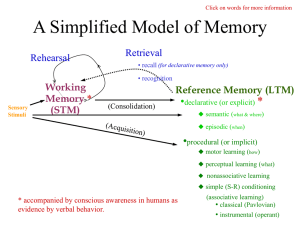
Physiological Psychology 41363 Outline 10 I.Learning and memory -learning - the process by which experiences change our NS and therefore our behavior: these changes are called memories -memory - dynamic mechanisms associated with the retention and retrieval of info abt past experience II. 4 basic types of learning A. Perceptual learning B. Stimulus - response learning 1. Classical (Pavlovian) conditioning 2. Instrumental (Operant) conditioning C. Motor learning D. Relational learning 1. spatial learning 2. episodic learning 3. observational learning III. Perceptual learning A. Perceptual learning is very fast B. Primary pathway for vision goes from the eyes, to the lateral geniculate nucleus of the hypothalamus and then to the primary visual cortex : this info is collected in the extrastriate cortex and sent to inferior temporal cortex where all the info is combined IV. S-R Learning A. Classical conditioning - (Pavlovian) 1. Components of classical conditioning a. A stimulus that evokes a particular response (Unconditioned stimulus; UCS) b. The automatic physiological response to the stimulus or UCS (Unconditioned response; UCR) c. A stimulus that is originally neutral to pair with the UCS (Conditioned stimulus; CS) d. After repeated pairings of the CS and the UCS, the CS will come to elicit the UCR itself known as the Conditioned response (CR) 2. Other aspects of classical conditioning a. higher order conditioning b. temporal characteristics B. Operant (instrumental) conditioning - learning behaviors based on the consequences of that behavior 1. Thorndike - 1890s Law of Effect 2. Skinner - Skinner boxes -reinforcer - increases the probability of a behavior -positive reinforcer -negative reinforcer -punishment - decreases probability of beh V. Relational learning - most of our memories are related to other memories A. H.M. -retrograde amnesia -anterograde amnesia B. H.M. is capable of 3 of the 4 types of learning 1. perceptual learning as evidenced by broken figure task 2. S-R learning - conditioned eyeblink 3. motor learning - mirror star trace C. Two different kinds of memories: 1. nondeclarative - perceptual, S-R, motor learning - learning we are not conscious of 2. declarative - those memories that are available to conscious recall VI. What causes anterograde amnesia? A. Damage to the hippocampus - the CA1 field of the hippocampus B. entorhinal cortex C. Lab animals with hippocampal lesions - place cells - pyramidal cells in the hippocampus: cognitive maps VII. How do these types of learning occur neuronally? A. Hebb rule - if a synapse repeatedly becomes active about the same time as a postsynaptic neuron, changes will occur in the synapse to strengthen it B. long-term potentiation: requires a series of pulses delivered at a high rate, low rate will not result in LTP -LTP is due to a glutamate receptor - NMDA receptor - found especially in field CA1 of the hippocampus C. How do we increase synaptic strengthening through LTP - NMDA-mediated LTP results in increases in sensitivity or number of postsynaptic glutamate receptors - calcium dependent enzymes called protein kinases