lazy notes - TeacherWeb
advertisement

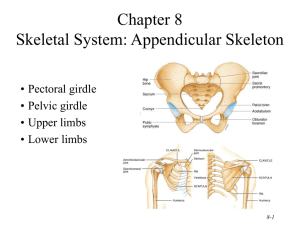
PECTORAL GIRDLE & UPPER ARM The pectoral girdle consists of two clavicles and two scapulae. These parts support the upper limbs and serve as attachments for various muscles that move these limbs. Each upper limb includes a humerus, a radius, an ulna, eight carpals, five metacarpals, and fourteen phalanges. These bones form the framework of the arm, forearm and hand. they also function as parts of levers when the limbs are moved. PECTORAL GIRDLE - Incomplete ring consisting of two scapulae and two clavicles: 1) attaches the upper limbs to the thoracic cage 2) site for muscle attachment 3) movement of the upper arm 1. Clavicle - Slender S-shaped bone (structurally weak-fractures easily if compressed lengthwise) Function - helps hold the shoulder in place by bracing the scapula Articulations: Acromial end (lateral) - ___________________________________________________ Sternal end (medial) - ____________________________________________________ 2. Scapula (shoulder blade) Articulations Glenoid cavity - ________________________________________________ Acromion process - _____________________________________________________ Features spine acromion process - forms the tip of the shoulder coracoid process glenoid cavity Borders superior border medial (vertebral) border lateral (axillary) border Fossae supraspinous fossa infraspinous fossa Why is the clavicle a bone that can easily fracture? THE UPPER LIMB Bones include the humerus, radius, ulna, 8 carpals, 5 metacarpals, and 14 phalanges 1. Humerus - extends from the scapula to the elbow Articulations Head - ____________________________________________ Capitulum - ________________________________________________ Trochlea - _________________________________________________________ Proximal features head greater tubercle lesser tubercle anatomical neck surgical neck - ____________________________________________________ intertubercular groove (sulcus) - _________________________________________________ Diaphysis deltoid tuberosity - _____________________________________________________________ Distal features capitulum trochlea medial condyle lateral condyle coronoid fossa - receives the coronoid process of the ulna _______________________________ olecranon fossa - receives the olecranon process of the ulna _____________________________ 2. Radius - located on the thumb side of the forearm, extending from the elbow to the wrist. Articulations head - humerus (capitulum) - ulna (radial notch) distal end - carpal bones Features head radial tuberosity - _______________________________________________ styloid process ulnar notch 3. Ulna - longer than the radius Articulations trochlear notch - ________________________________________ radial notch - ____________________________________________________ head - fibrocartilage disc inferiorly - _______________________________________ Ulna - Features olecranon process - triceps brachii inserts here; fits into the _____________________________ coronoid process - fits into the coronoid fossa of the humerus ___________________________ styloid process head THE HAND `1) The wrist - 8 carpal bones (form the carpus) 2) The palm - 5 metacarpal bones 3) the 5 fingers - 14 phalanges (3 in each finger; the thumb lacks the _______________________ 1. Carpal bones Proximal row (listed lateral to medial) scaphoid lunate triquetrum pisiform Distal row (listed medial to lateral) hamate capitate trapezoid trapezium *Mnemonic for remembering the names of the carpal bones: So Long To Pinkie (proximal row, lateral to medial) Here Comes The Thumb (distal row, medial to lateral) 2. Metacarpal bones - ___________________________________________________________ 3. Phalanges proximal phalanx middle phalanx distal phalanx