File - Pomp
advertisement

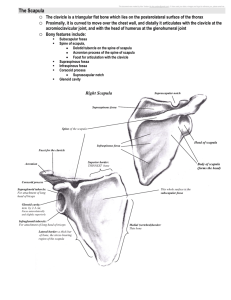
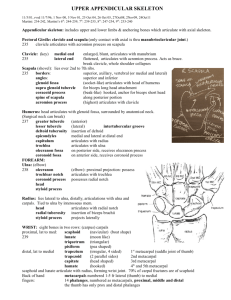
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Pectoral Girdle General anatomical terms to know Process Ramus Trochanter Tuberosity Tubercle Crest Line Spine Head Neck Condyle Trochlea Facet Fossa Sulcus Foramen Canal of meatus Fissure Sinus Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Includes bones of the limbs (appendages) Supporting bones of the pectoral and pelvic girdles (connect limbs to axial skeleton) Pectoral Girdle forms the shoulder Consists of two bones clavicle (collarbone)- long bone 1. 1. Latin word “clavicula” = little key scapula (shoulder blade) 2. Allows free movement of upper limb Sternoclavicular joint – where the clavicle meets the sternum Acromioclavicular joint – where the clavicle meets the scapula Loose attachment allows scapula to move freely Shoulder joint is poorly reinforced by ligaments Easily dislocated Right Pectoral Girdle - Anterior Right Pectoral Girdle -Posterior The Clavicle Aka Collarbone Slender, doubly curved bone Acts as a brace to hold the arm away from the thoracic cage Helps prevent shoulder dislocation Structures to know: Acromioclavicular joint and sternoclavicular joint The Clavicle The Scapula Aka Shoulder blade (little shovel) Anatomy: Flattened body Spine (posterior) Supraspinous Origin of the supraspinatus muscle (rotator cuff) (posterior) Infraspinous fossa – Inferior to (below) the spine Origin of the supraspinatus muscle (rotator cuff) (posterior) Additional Fossae: Subscapular fossa – Superior to (above) the spine fossa- anterior Origin of the subscapularis muscle (rotator cuff) (anterior) The Scapula Acromion process = enlarged end of the spine of the scapula Articulates with the clavicle to form the acromioclavicular joint Comes from the Greek word “Akron”(peak) and “Omos”(shoulder) Coracoid process = “beak”-like process Suprascapular notch = nerve passageway Points over the top of the shoulder and anchors arm muscles Forms a foramen (ossification of transverse ligament) that provides passage way for the suprascapular nerve. Glenoid fossa(cavity) = shallow socket that receives the head of the arm Comes from the greek work “glene” (socket) The Scapula Borders: Lateral (axillary) border Medial (vertebral) border Superior border The Scapula- posterior aspect Coracoid process Suprascapular notch acromion spine Medial border Lateral border The Scapula- anterior aspect acromion Suprascapular notch Coracoid process Glenoid Cavity Lateral border Medial border Scapula THE UPPER LIMB Bones of the Upper limbs 30 separate bones in each upper limb Arm, foreharm, hand The arm The humerus – single typical long bone of the upper arm Articulates proximally with scapula and clavicle and distally with radius and ulna Proximal features: Head – fits into glenoid cavity of scapula Greater and lesser tubercles – two bony projections lateral to the head Separated by the intertubercular sulcus Attachment of tendons Anatomical neck – slight constriction just inferior to the head Surgical neck – most frequently fractured part of the humerus Features of the diaphysis: Features of the diaphysis (shaft): Deltoid tuberosity: attachment for the deltoid(shoulder) muscle Radial groove- marks the course of the radial nerve The arm Distal features: Lateral and medial epicondyles: External and internal condyles: Olecranon fossa: groove that receives the olecranon process of the ulna upon extension of the arm. Coronoid fossa: groove that receives the coronoid process of the ulna upon flexion of the arm. Trochlea (medial) articulates with trochlear notch of the ulna. Capitulum (lateral) articulates with head of the radius The right arm (humerus) Greater tubercle Lesser tubercle Intertubercular Sulcus head Anatomical Neck Surgical Neck The right arm (humerus) Greater tubercle Greater tubercle Lesser tubercle Intertubercular Sulcus head Anatomical Neck Surgical Neck Radial Groove Deltoid tuberosity Deltoid tuberosity Coronoid fossa Olecranon fossa Radial fossa capitulum Medial Epicondyle trochlea Lateral Epicondyle The forearm Consists of two bones 1. 2. Radius = lateral bone when in anatomical position Ulna = medial bone when in anatomical position Radioulnar joints = sight of articulation of radius and ulna Two bones are connected along their entire length by interosseous membrane Structures to know: radial tuberosity, styloid process, coronoid process, olecranon process, trochlear notch Trochlear Notch head neck Radial tuberosity Olecranon Process Coronoid Process Proximal Radioulnar joint Radius Ulna Interosseous membrane Styloid Process (radius) Styloid Process (ulna) Distal Radioulnar joint The Hand Wrist (carpals) = 8 short bones Palm (metacarpals) = 5 long bones Fingers (phalanges)= long bones Thumb has 2 phalanges Each finger has 3 phalanges Proximal phalange Medial phalange Distal phalange Phalanges Metacarpals Carpals hamate trapezium pisiform triquetrum trapezoid scaphoid lunate Ulna capitate Radius 1. Can you identify the following?? 2. 5. 3. 6. 4. 7. 8.