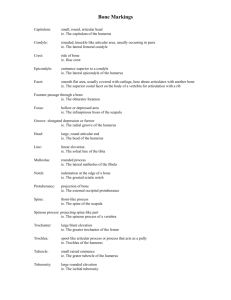
Block 3-6 Osteology and Arthrology of the Humerus, Elbow, and

Block 3-6 Osteology and Arthrology of the Humerus, Elbow, and Shoulder Girdle
1.
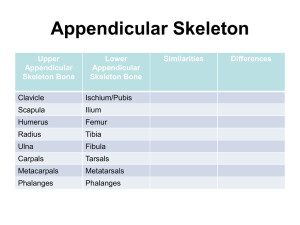
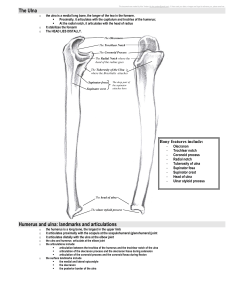
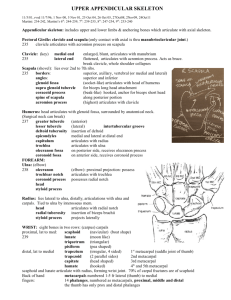
Distally the humerus articulates with the radius and ulna to form the _____. a. Hand b. Elbow joint c. Shoulder d None of the above
2.
The Trochlea is a spool like structure on the distal end of the humerus and articulates with the radius. a. True b. False articulates with the ulna
3.
Which one of the following is referred to as a marble-like process on the anterolateral surface of the distal humerus? a. Lateral epicondyle b. Medial epicondyle c. Capitulum d. Coronoid fossa
4.
________ is a large depression on the posterior surface and articulates with the olecranon process and prevents hyperextension. a. Coronoid fossa b. Olecranon fossa c. Lateral epicondyle d. Capitellum
5.
The Bicipital sulcus is a groove for tendon passageway on the anterior aspect proximal end of the humerus. a. True b. False
6.
How many bones make up the elbow joint? a. One b. Two c. Three d. None
7.
Which one of the following are formed by the head of the radius and capitulum of the humerus. Their main responsibility is to add stability to the joint.
a. Radial head and Capitulum b. Coronoid process and Coronoid fossa c. Trochlea and Semi-lunar notch d. Olecranon process and Olecranon fossa
8.
Which bone acts as a strut or brace to maintain the position of the shoulder.
Located in the superior anterolateral portion of the thorax. a. Humerus b. Clavicle c. radius d. ulna
9.
The sternal (medial) rounded end of the clavicle articulates with the sternum to for the ______. a. A-C joint b. S-C joint c. shoulder joint
10.
Which joint is formed by the medial end of the clavicle and the manubrium of the sternum? a. Sternoclavicular joint b. Acromioclavicular joint c. Glenohumeral joint d. None of the above