The Crisis of Reconstruction, 1865-1877
advertisement

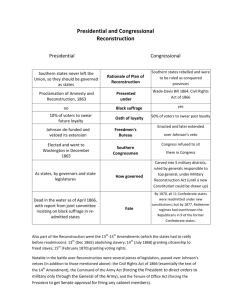
The Crisis of Reconstruction, 1865-1877 The biggest fight after the war was political ◦ Power struggles between the executive and legislative branches ◦ Constitutional amendments ◦ Presidential impeachment ◦ Ambitious domestic legislation Only a small group supported black suffrage Lincoln’s Plan Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction ◦ 10% of those who had cast ballots in 1860 ◦ A loyal state govt. would be created ◦ Excludes: Confederate govt. officials, army/navy officers, those who resigned commissions in 1861 (they would apply for a pardon), blacks This 10% Plan would undermine Confederacy with pro-Union govts. He wants to win allegiance of southern Unionists and rebuild a Southern Republican Party Radical Republicans think Lincoln’s plan is too weak They want to punish more Confederates July 1864: Wade-Davis Bill ◦ Each southern state to be ruled by a military governor ◦ 50% plan for readmittance after they repeal secession and abolish slavery ◦ Second “ironclad” oath to qualify as a voter/delegate Lincoln pocket vetoes the bill By the war’s end AK, LA, TN, and parts of VA had moved towards readmittance under Lincoln’s plan Congress refuses to seat the delegates Presidential Reconstruction Under Johnson Johnson was the only southern senator to remain in Congress when his state seceded Johnson despised the planter class During Congress’s recess Johnson announces how the seven remaining states can be readmitted: ◦ Almost all who take an oath may return ◦ All property except slaves will be restored ◦ State conventions would have to claim the illegitimacy of secession, repudiate state debts, and ratify the 13th Amendment ◦ Also, wealthy Confederates (over $20,000) barred Johnson handed out 13,000 pardons Confederate officers and large planters assumed state positions Even VP Stephens went to DC as a senator States enact Black Codes to get around the 13th Amendment When Congress reconvenes in December of 1865 they refuse to seat the new delegates and establish the Joint Committee on Reconstruction ◦ It is now Congress vs. Johnson Congress vs. Johnson Status of southern blacks is now the key issue Moderate Republicans were the largest bloc in Congress; they agreed that Johnson’s plan was weak They joined up with the Radicals in the following ways ◦ Continuation of the Freedman’s Bureau 3-yr. extension; special military courts to settle labor disputes ◦ Passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1866 (over Johnson’s veto) Blacks are citizens and it authorized the feds to intervene in states to ensure black rights in the courts 1st major piece of legislation passed over a presidential veto Johnson vetoed because he felt it illegitimate because the South had been cut out The Fourteenth Amendment April 1866: Naturalization, due process, equal protection Nullifies Dred Scott States who deny male suffrage can lose representation in Congress Disqualifies from office all prewar officeholders Repudiates Confederate debt and maintains validity of federal debt This was the first national effort to limit state control of civil and political rights Congressional elections of 1866 were a referendum on the 14th ◦ Republicans win 2/3 of the House; 4/5 of the Senate Congressional Reconstruction Congress passes Reconstruction Acts over Johnson’s vetos Reconstruction Act of 1867 ◦ Invalidated the state governments formed under Lincoln and Johnson (except TN) ◦ Set up five military districts ◦ Blacks and whites could elect delegates to set up new constitutions ◦ Then elect state officers ◦ Congress approves the state constitution, state leg. Ratifies the 14th, readmittance This act was harsher than Johnson, but did not prosecute Confederates for treason, or permanently exclude them from politics Also, it didn’t redistribute land ◦ Even Republicans didn’t want to mess with the sacredness of property rights Impeachment Crisis Tenure of Office Act and a rider to an army appropriations bill Johnson fires Sec. of War Stanton Why not removed? ◦ Removal would upset the balance of power ◦ Afraid of the Pres. Pro Tempore Fifteenth Amendment and the Question of Woman Suffrage The need to make black suffrage national Ratified in 1870 – The south didn’t have enough votes to block it Women’s movement splits into two organizations ◦ American Woman Suffrage Assoc. – states ◦ National Woman Suffrage Assoc. – national (Stanton and Anthony) ◦ Minor v. Happersett – the state can deny women the right to vote A New Electorate Laws had disenfranchised 10-15% Blacks held voting majorities in five states Carpetbaggers, scalawags, and freedmen ◦ Carpetbaggers: no more than 20,000 ◦ Scalawags: mostly small farmers that cared little for black rights ◦ Freedmen: the backbone of southern Republicanism (8 or 10 Rep. votes) At most1 in 5 political offices; in all southern legislatures; majority in South Carolina; two senators; no Governors; 6% of the House (half from South Carolina) Republican Rule No state instituted land reform Politicians wanted to attract northern investment Shift towards public works projects Increased taxes to pay for rebuilding Reconstruction was punishing the propertied Counterattacks Vigilante groups spring up in all southern states There is an effort to deny blacks participation in government Intimidation, purchase, killing, etc. 1866- the KKK is formed Federal govt. responds with the Enforcement Acts (1870 and 1871): these allow federal supervision and protection Shows that federal supervision was necessary, but it was never going to happen on a large scale Feds let the Freedman’s Bureau end in 1869 Confronting Freedom House slaves were more likely to flee the plantation than field slaves Most moved to adjacent plantations During the 1860s urban black population increased by 75% Seeking family was prominent So was the legalization of unions and quickly established two-parent families Black women seek female roles Black Institutions Growth of the Black Church, esp. the African Methodist Episcopal Church and Black Baptist churches Churches and ministers become the pillars of black society Black schools were set up by the Freedman’s Bureau and northern philanthropic societies Traditional black colleges such as Howard, Atlanta, Fisk and Hampton all formed However, by the end of Reconstruction 80% of black pop. is still illiterate 1883 Civil Rights cases: 14th amendment did not prohibit discrimination by individuals A segregated society is developing, and is supported by both races Land, Labor, and Sharecropping Forty acres and a mule never really happened 1866: Southern Homestead Act ◦ 44 million acres set aside in five state ◦ Bad land and few made it work Blacks had no capital; no whites would sell them land anyway; labor contracts were unjust By 1880, 80% of land in cotton producing states is sharecropped Crop-lien system comes into existence Both sharecropping and the croplien system prevent diversification of southern agriculture Grantism Grant is elected in 1868: Carried all but eight states due to his popularity in the North; being unscathed by Reconstruction politics; and the black vote in the South His administration was riddled with scandals ◦ Cornering the gold market, Credit Mobilier, “Whiskey Ring,” and Indian trading posts Grant may have not known all of these, but it was the Gilded Age Foreign policy issues ◦ Seward’s Icebox ◦ Attempt to annex the eastern half of Santo Domingo (Senate rejects this) ◦ By 1872, Liberal Republicans form their own party to get away from Grantism and the “Great Barbeque” Liberals’ Revolt Liberal Republicans believed in free trade, the gold standard, and the law of supply and demand. They demanded civil service reform, the end to bayonet rule in the South, the end of high tariffs They nominate Horace Greeley and lose Grant then supports the Amnesty Act to undercut the Liberals views on the South Panic of 1873 The Transcontinental Railroad in complete and over speculation in RR begins The collapse of the Northern Pacific Railroad triggered a financial meltdown in America (5year depression) 18,000 businesses go bankrupt; 3 million unemployed Money and the debt What to do with the greenbacks? How to pay off the debt? Reconstruction and the Constitution Ex parte Milligan decision dooms the military courts established to enforce the Freedman’s Bureau Texas v. White – Reconstruction was constitutionally possible, grounded in the Congressional power to provide a republican form of government to every state Slaughterhouse cases of 1873 – chipped away at the 14th Amendment by narrowly defining it Republicans Retreat It was gradual, but it happened ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Grant’s elections The rise of the Liberal Republicans The Amnesty Act Supreme Court decisions Radicals had left the scene Industrial expansion Just plain tired of it Redeeming the South Democrats a beginning home rule again But it is New South advocates vs. the Bourbons The White League; Mississippi plan; Red Shirts; Rifle Clubs were effective Once the redeemers were back in power they rewrote the laws to diminish freedmen’s rights, as well as their economic, political and social standing Late 1870 “exodusters” to Kansas Election of 1876 Hayes (R) vs. Tilden (D) Platforms were very similar Tilden wins the popular vote by 3%; however 19 electoral votes in South Carolina, Florida, and Louisiana (proTilden) were challenged, and 1 in Oregon (pro-Hayes) Republicans controlled the three proTilden states so those were thrown out; but Democrats had kept blacks from voting Neither had enough Electoral Votes Compromise of 1877 ◦ Commission of 7 Dems., 7 Rep. and 1 Independent to decide ◦ The Ind. Resigns to run for the Senate and his position is filled with a Republican ◦ Hayes wins! ◦ Not so fast: The Dems. Controlled the House, and they were going to obstruct the approval of Electoral votes ◦ A deal had to be cut The Basic Deal ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Hayes gets to be President Troops are taken out of the South Democrats are back in charge Reconstruction ends