Section Two: Congressional Reconstruction
advertisement

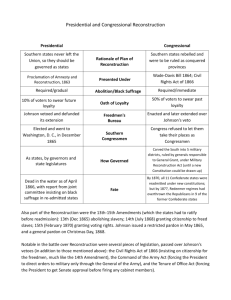
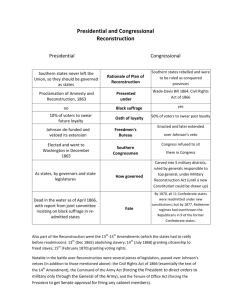
US History II - Reconstruction Congressional Reconstruction Johnson Takes Office - assassination of Lincoln – dramatic changes to the politics - vice president Andrew Johnson became president - believed in moderate policy to bring South back into Union - Johnson’s Plan o summer of 1865 – restoration program – closely resembled Lincoln’s o May 1865 – new Proclamation of Amnesty – offered to pardon all former citizens of Confederacy – took an oath of loyalty to the Union o excluded – former Confederate officers & officials – as well as those who owned property more than $20,000 o former states met Johnson’s conditions o Congress opened in Dec 1865 – Johnson’s plan underway – members of Congress angered that former Confederates were members of Congress – voted to reject them - Black Codes o Southern state legislatures passed a series of laws known as black codes – severely limited African Americans’ rights in the South o codes varied – intended to keep African Americans in a condition similar to slavery – enraged Northerners Radical Republicans Take Control - election of former Confederates to office & intro of black codes convinced many moderate Republicans to join the Radicals - late 1865 – House & Senate Republicans created the Joint Committee on Reconstruction goal develop their own rebuilding plan for the Union - The Fourteenth Amendment o March 1866 – Congress passed Civil Rights Act of 1866 o granted citizenship to all persons born in the US except Native Americans o Fourteenth Amendment – granted citizenship to all persons born or naturalized in the US & declared that no state could deprive any person of life, liberty, or property “without due process of law” - The Election of 1866 o Johnson attacked the 14th Amendment – made it a major issue of the 1866 congressional elections – wanted the Northern voters to turn against the Radical Republicans – elect a new majority 1 US History II - Reconstruction - - - - o Republicans won a three to one majority in Congress Military Reconstruction o March 1867 – Military Reconstruction Act passed – got rid of Johnson’s plan o divided former Confederacy into 5 military districts (except Tenn. ratified 14th Amendment) – Union generals placed in charge of them o new state constitutions had to give the right to vote to all adult male citizens – regardless of their race o had to ratify the 14th before they could elect members to Congress o end of 1868 – 6 states met all requirements – NC, SC, Fl, Al, LA, AK Impeachment o Republicans had enough votes to override any veto – also felt they had the support of Sec of War Stanton & General Grant o Command of Army Act – required all orders from president to go thru headqrters of general of the army o Tenure of Office Act – required the Senate to approve the removal of any gov’t official – whose appointment had required Senate’s consent o Johnson fired Stanton on Feb 21, 1868 –refused to leave his office o Feb 24 – House of Representatives voted to impeach Johnson – had broken the law by refusing to uphold Tenure of Office Act – removed four commanders in Southern military districts undermining Reconstruction program o on trial – on May 16, 1868 – Senate voted 35 to 19 – one vote short of what was needed to impeach him The Election of 1868 o candidate for Republicans – General Grant o ongoing violence in South o presence of Union troops in south enabled African Americans to vote in large numbers o Grant won 6 southern states & most northern states The Fifteenth Amendment o Radical Republicans moved quickly on their reconstruction plan o 15th – declared the right to vote “shall not be denied…on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude” o March 1870 – enough states had ratified it – made it part of Constitution 2