Article I Section 5 US Constitution
advertisement

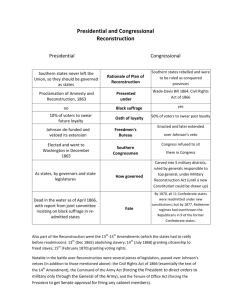
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Reconstruction What you “Gotta” know Civil War ends on paper April 1865 - Lincoln assassinated 10% Plan to quickly reunite the nation in doubt Andrew Johnson, VP from Tennessee, becomes US President “Radical” Republicans in Congress create the Wade-Davis Bill A punishment for secession and assassination of Lincoln Johnson and Congress wrestle with Reconstruction plans As Congress and Johnson squabble – Southern states begin to resort to old lifestyle Black codes put in place – a new form of slavery Johnson demands that all former confederate officials petition him directly for a pardon December 1865 – Johnson declares Reconstruction complete Radical Congress disagrees – Refuses to seat newly reelected and former confederate officers into Congress Article I Section 5 US Constitution - Membership, Rules, Journals Each House shall be the Judge of the Elections, Returns and Qualifications of its own Members Congressional Republican consolidate power and are able to override any Presidential veto Johnson known as the “Dead Dog of the White House” Radical Reconstruction now in place – Civil Rights Act of 1867 Former confederacy split into 5 military districts No former confederates allowed to vote or hold office All states must pass 14th Amendment Any person born in US is a citizen of the US All states must guarantee all black males the right to vote 1868 Radicals attempt to impeach Johnson – Tenure of Office Act Can the President fire government officials confirmed by the Senate? Impeachment fails by 1 vote Later, SC declares Tenure of Office Act unconstitutional 1869 - 15th Amendment passed – Guarantees voting rights for all black males 1870 – former slaves elected US House and Senate – Hiram Revels elected to seat formerly held by Jefferson Davis, former Confederate President Election of 1876 – Republicans agree to remove US troops from South in return for Florida electoral votes – Reconstruction officially ends New issues dominate politics; country tired of Civil War Legacy of Reconstruction Emergence of KKK - 1866 Segregation and Jim Crow Laws – reemergence of white power Women still not given voting rights Plessey v. Ferguson 1896 – Separate but equal is Constitutional