Reconstruction - Loudoun County Public Schools
advertisement

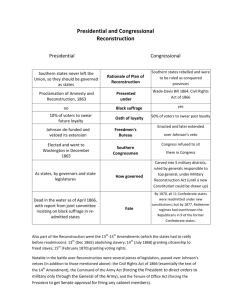
RECONSTRUCTION Chapter 16 After the Civil War South is destroyed: Economically Physically Spiritually Major Questions: How could Union be restored? How would South be reintegrated? How should Confederate states be treated? Who would control readmission? Would Confederate leaders be punished? What would happen to former slaves? Lincoln’s Plan 10% Plan (1863) When 10% of state’s citizens took loyalty oath and accepted emancipation, state could set up government Excluded from oath: Confederate government officials and officers (could apply for Presidential Pardon) Opposition Thaddeus Stevens Ben Wade Charles Sumner Wade-Davis Bill Passed July 1864 Each state ruled by military government 50% of eligible voters had to take oath State convention had to repeal secession and abolish slavery To earn voting rights would have to swear to 2nd “iron-clad” oath Lincoln vetoed Radical Republicans Thought Lincoln’s plan was too lenient Lincoln’s Death Dies before he could implement any plan Johnson’s Plan Favored Lincoln’s moderate approach Created plan while congress out of session All southerners who took oath would receive a pardon and amnesty with all property restored Could elect delegated to state convention Excluded Confederate officials and officers As well as, ex-confederates with 20,000+ in taxable property Way to purge aristocracy Consequences Johnson handed out pardon liberally (13,000) Dropped plan for punishment of treason All established governments by December 1865 Confederates elected to office/congress Some refused to ratify 13th amendment or repudiate debts South’s Black Codes Black Codes Guaranteed basic rights Enforced segregation in public places Prohibited interracial marriage, jury service by blacks, court testimony of blacks against whites Barred slaves from leaving former plantations Most didn’t go into effect Marry, own property, contracts, testify Union Army Freedman’s Bureau Thought of southern defiance Freedman’s Bureau Created March 1865 Early Welfare agency Relief Rations Medical care Protect blacks rights as laborers By Congress Also protected/ helped poor whites Military courts to settle disputes Greatest Success = Education 3,000 schools + black colleges Taught 20,000 to read by 1870 Sea island experiment Congress v. Johnson Conflict Radical Republicans Minority in congress Thaddeus Stevens Conservative Republicans Wants black suffrage and to delay readmission of Confederate states Minority in congress Favored Johnson’s plan Moderate Republicans Largest bloc in Congress Thought Johnson’s plan too weak Didn’t want black suffrage Supported two proposals: Senator Trumbull Invalidate black codes Bill to make blacks US citizens and ensure rights in court 1866 called Civil Rights Act Johnson vetoed, Congress over-rode Mid-term Elections 1866 Johnson “swing around the circle” Appealed to whites Argued equal rights would = Africanized society Tried to attack Congress Republicans Accused Johnson as traitor “waving the bloody shirt” Reminded hardships North of war Results: Overwhelmingly a Republican victory in both houses th 14 Amendment, 1866 Proposed by joint committee on reconstruction Clauses Citizens All persons born or naturalized in US No state could abridge blacks rights without due process Guaranteed suffrage by threatening republicans in Congress Disqualified those who supported Confederacy South had to be forced to deal with blacks fairly Issue in 1866 elections Republicans succeeded Enough members to force any legislation Congressional Reconstruction, 1866-1867 Radicals wanted: Black suffrage Federal support for schools Confiscation of Confederate estates Period of military occupation of South Passed 1867; Reconstruction Act Johnson vetoed, congress passed over Invalidated state governments under Lincoln and Johnson 5 military districts, run by Union generals Enfranchised blacks Slowed readmittance of Confederate states No treason or confiscation of property Thaddeus Stevens wanted to take property and split into 40 acres and give to freedmen Didn’t pass because of issues of property rights Impeachment Crisis, 1867-1868 March 1867 Congress passes two laws to limit presidential power Tenure of Office Act Couldn’t remove civil officers without senate consent Barred Johnson from issuing military orders except through commanding general August 1867 Johnson suspended secretary of war Stanton Wants to replace with Grant Senate refused to approve Impeached him Trial March 1868: not guilty Circus like atmosphere Election of 1868 Republican Ulysses S. Grant Famous Union General No political experience Democrat Horatio Gov. Seymour from NY Results Grant wins Mainly due to 500,000 black votes Only won Pop vote by 300,000 th 15 Amendment (3 rd “Reconstruction” Amendment) Republicans NEEDED black voters support 1869: 15th amendment proposed loopholes: Did not guarantee office holding Did not prohibit voting restrictions Question of women’s rights Two groups: Boston American Women’s Suffrage Association Julia Ward Howe, Lucy Stone New York National Woman Suffrage Association Stanton, Anthony More radical, wanted amendment Legislation: Declared a state could deny woman right to vote Minor v. Happersett (1875) Reconstruction Governments New Electorate Blacks held majority in Southern states Carpetbaggers Scalawags freedman Black Officeholders= elite Literate, non-slaves Republican Rule Counterattacks Southern Republicans base of Republican party No state instituted land reform Ambitious public works at state levels Created public school systems State debt/ taxes skyrocketed Didn’t act until states admitted to Union 1870 Enforcement Act Protect black voters 1871 2nd Enforcement Act Federal suspension 3rd Enforcement Act of elections (KKK) Strengthened punishments Use of federal troops Suspension of habeas corpus Impact of Emancipation Changes to life Waves of migration Sharecropping Urban movement Find family Freedman’s Bureau Family life Legalize unions Traditional roles Black Institutions Growth of black churches Ministers assumed political roles Black schools Segregated public schools Rejected integration Black universities Remained limited, underfunded Southern Homestead Act 1866 44 millions acres in SC/GA Poor soil, no resources Unable to establish Lacked $ and equipment White didn’t want to sell to blacks Planters wanted to preserve black labor force Black codes Labor contracts 1866 “work your way up” Problems Bad harvests, price dropping = sharecropping Rents for share of crop Landowners still retained power Depression of 1873 Lots of debt Crop-Lien Economy Needed more localized network of credit Merchants sold supplies, equipment on credit No collateral, used claimed on next crop Cycle of indebtedness Transformed southern agriculture Prevented crop diversification Cash crops Soil depletion, land erosion poverty New Concerns in the North, 1868-1876 Grantism War hero Endorsed by Union Vets Passive President Plagued by scandals Rise of the Spoilsmen Roscoe Conklin, James Blaine Credit Mobilier Affair Whiskey Ring Republicans worried about election of 1872 Formed Liberal Republican Party Revolt Seward’s Folly 1867 $7.2 Million Grant Turning point in Recon. Split support for Reps. “Liberal” Grantism, civil-service reform, high tariff policy, Bayonet rule in South Nominated Horace Greely Dominican Republic unsuccessful Free trade, gold standard, supply/demand Attacked Johnson Boss Tweed Foreign policy Liberal Revolt Democrats endorsed “anything to beat Grant” Worked himself to death Grant wins = landslide Panic of 1873 Post-war industrial boom Transcontinental railroad 1869 over speculation Consequences Jay Cooke (Union Pacific) 1873 costs outrun investments By Sept. couldn’t meet obligations Banks shut down Panic Industrialization issues now replaced sectionalism Currency Dispute Greenbacks withdrawn after war Farmers wanted easy money Issue divided Rep. party National Debt Public Credit Act 1869 (Sherman) Other banks shut down Stock market collapsed 5 yr depression Pay back war bonds in coin Swap for new ones 1872 “gold coin” 1875 Specie Resumption Act Politics Democrats win house 1875 Greenback party 1876 No answer to money question Reconstruction and the Constitution Supreme Court Weakened northern support Ex Part Milligan 1866 Court would not support congressional laws to protect freedman’s rights Special military courts to enact Enforcement Act 1870 Undercut effectiveness Texas v. White 1869 Restoring states meaningless because union was indissoluble Slaughterhouse Cases 1873 Chipped away at 14th amendment Over monopolies States could violate rights U.S. v Reese and U.S. v. Cruikshank 1875 Consequences Invalidated Civil Rights Act of 1875 KKK Act of 1875 End of Reconstruction Republicans in Retreat Grant reluctant to assert federal authority in state and local affairs 1870’s idealism waned 1872: Amnesty Act Commercial and industrial interests more important 1874: Democrats win elections 1875 Radical Republicans disappeared Reconstruction abandoned Redeeming the South Equal accommodations in public places Poor enforced Old planter elite One goal: Oust Republicans from office Industrialized New South Bourbons Last Civil Right Act of 1875 Businessmen 1876-1877 Democrats gained momentum after Amnesty Acts Mobilized formerly apathetic white voters Divided party Used intimidation White leagues, Miss. plan Exodus movement “Kansas Fever” 1879 Election of 1876 Republican Rutherford B. Hayes “moderate” on southern policy, Home-rule Untainted by Grant Guaranteed civil and political rights for all Democrat Samuel Tilden Campaigned against fraud and waste Both: Boss Tweed Fiscal conservatives Favored sound $ Decried corruption Election: Corrupt Challenged Tilden’s victory Electoral Commission 1877 Hayes Win, Democrats the House “Compromise of 1877” Election cartoons Evaluating the Republican Record Accomplishments Liberalized state constitutions in South Universal male suffrage Property rights for women Debt relief Promoted building of roads, bridges, railroads, and other internal improvements Est. state institutions such as hospitals, asylums State-supported school systems Failures Corruption Wasteful spending Bribes/ kickbacks The North During Reconstruction Rise of the Spoilsmen Corruption in business and government Scandals Boss Tweed Stole $200 million from taxpayers in NY Battle between Tweed and Thomas Nast Arrested in 1871 Reconstruction Summary Reconstruction a democrat experiment that didn’t go far enough Congress did not promote freedman’s independence through land reform Federal government neglected to back Congressional Reconstruction with military force Failure of government to fulfill its own goals Looking towards a new America