Management
Accounting: The
Cornerstone for
Business Decisions
Job-Order Costing
Copyright ©2006 by South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning. All rights reserved.
Learning Objectives
1. Describe the differences between joborder costing and process costing and
identify the types of firms that would
use each method.
2. Compute the predetermined overhead
rate and use the rate to assign overhead
to units or services produced.
3. Identify and set up the source
documents used with job-order costing.
Learning Objectives
4. Describe the cost
flows associated
with job-order
costing..
5. (Appendix)
Prepare the
journal entries
associated with
job-order costing.
Distinguish Between JobOrder and Process Costing
Job-Order Costing
Process Costing
What are the three costs of
production?
Define Normal and Actual
Costing
◙ Normal costing
◙ Actual costing assigns
Complete the Table with
Either Actual or Applied
Normal
Direct
Materials
Direct
Labor
Overhead
Actual
Discuss the Importance of
Unit Costs
5-1
How to calculate the
predetermined overhead rate.
At the beginning of the year, Argus
Company estimated the following costs;
Overhead
$480,000
Direct labor cost
$960,000
Argus uses normal costing and applies
overhead on the basis of direct labor cost.
(Direct labor cost is equal to total direct
labor hours worked multiplied by the
wage rate.) For the month of March, the
direct labor cost was $62,000.
5-1
How to calculate the
predetermined overhead rate.
REQUIRED:
1. Calculate the predetermined overhead
rate for the year.
2. Calculate the overhead applied to
production in March.
Calculation:
Comment on the Two Types
of Overhead
How to reconcile actual overhead
5-2
with applied overhead.
At the beginning of the year, Argus Company
estimated the following costs;
Overhead
$480,000
Direct labor cost
$960,000
At the end of the year, the actual data are:
Overhead
$480,500
Direct labor Cost
$982,000
Argus uses normal costing and applies overhead
on the basis of direct labor cost. A the end of
the year, Cost of Goods Sold (before adjusting
for any overhead variance) is $842,000.
How to reconcile actual
5-2 overhead with applied overhead.
REQUIRED:
1. Calculate the overhead variance for the
year.
2. Dispose of the variance by adjusting Cost
of Goods Sold (COGS).
Calculation:
How to reconcile actual
5-2 overhead with applied overhead.
Overapplied and
Underapplied Overhead
5-3
How to calculate predetermined
departmental overhead rates and
apply them to production.
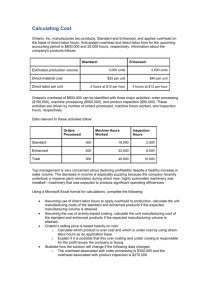
At the beginning of the year, Sorrel Company estimated the
following;
Machining Assembly Total
Overhead
$240,000
$360,000
$600,000
Direct labor hours 135,000
240,000
375,000
Machine hours
200,000
200,000
Sorrel uses departmental rates in the machining department,
overhead is applied on the basis of machine hours. In the
assembly department, overhead is applied on the basis of
direct labor hours. Actual data for the month of July are as
follows:
Machining Assembly Total
Overhead
$22,000
$33,000
$55,000
Direct labor hours 11,500
22,400
33,900
Machine hours
16,900
16,900
5-3
How to calculate predetermined
departmental overhead rates and
apply them to production.
REQUIRED:
1. Calculate the predetermined overhead
rate for the machining and assembly
departments.
2. Calculate the overhead applied to each
department for the month of July.
3. By how much has each department’s
overhead been overapplied?
Underapplied?
Calculation:
5-3
How to calculate predetermined
departmental overhead rates
and apply them to production.
Calculation:
Machining
Actual Overhead
Applied Overhead
Under(Over)applied
Overhead
Assembly
5-4
How to convert departmental data to
plantwide data to calculate the overhead
rate & apply overhead to production.
At the beginning of the year, Sorrel Company estimated the
following:
Machining Assembly Total
Overhead
$240,000
$360,000
$600,000
Direct labor hours 135,000
240,000
375,000
Machine hours
200,000
200,000
Sorrel has decided to use a plantwide overhead rate based on
direct labor hours. Actual data for the month of July are as
follows:
Machining Assembly Total
Overhead
$22,000
$33,000
$55,000
Direct labor hours 11,500
22,400
33,900
Machine hours
16,900
16,900
5-4
How to convert departmental data to
plantwide data to calculate the overhead
rate & apply overhead to production.
REQUIRED:
1. Calculated the predetermined plantwide
overhead rate.
2. Calculated the overhead applied to
production for the month of July.
3. Calculate the overhead variance for the
month of July.
Calculation:
Define a Job-Order Cost
Sheet
What is a materials
requisitions form?
Accounting for the Flow of Costs
Finished Goods
Warehouse
Materials
Inventory
Work-inProcess
Accounting for Overhead
◙ Since most businesses use normal
costing, they apply overhead using a
predetermined overhead rate.
◙ Actual overhead is recorded but NEVER
recorded in the Work-in-Process.
◙ Actual overhead is recorded in a control
account.
◙ Actual overhead and applied overhead
are reconciled at the end of the period.
Produce a Schedule of Cost
of Goods Manufactured
Prepare a Statement of Cost
of Goods Sold
Prepare an Income Statement
Prepare entries for Johnson
Leather Goods for February
1. Purchased raw materials on account, $3,350.
2. Requisition materials for use in production,
$3,500.
3. Recognize direct labor costing $2,520. Show
as a liability in wages payable.
Prepare entries for Johnson
Leather Goods for February
4. Applied overhead to production a the rate of
$2 per direct labor hour. A total of 280 direct
labor hours were worked.
5. Incurred actual overhead of $535.
6. Completed the saddlebags job and
transferred to finished goods.
Prepare entries for Johnson
Leather Goods for February
7. Sold the saddlebags job at cost plus
60%.
8. Closed overapplied overhead to Cost of
Goods Sold.