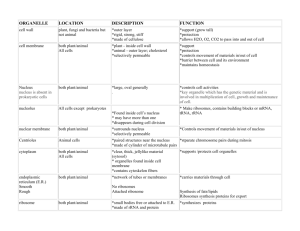
Plant and animal cells
advertisement
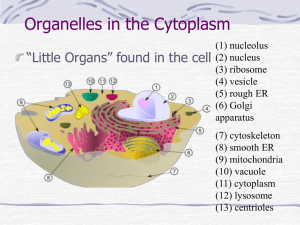
7-2: Eukaryotic Cell Organelles Stem cells White blood cell trapping bacteria Skin cells • The cell is divided into 2 parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. • The nucleolus is in the nucleus • Everything else is in the cytoplasm. • Plant cells: have cell walls & chloroplasts • Animal cells don’t Nucleus • Acts like the control center of the cell. • Contains the DNA that holds the genetic code for making proteins. • Surrounded by the nuclear envelope. Nucleolus • A small dense region within the nucleus. • Where the assembly of ribosomes begins. Ribosomes • Ribosomes can float freely in the cytoplasm or be attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. • They assemble the proteins for the cell. Endoplasmic reticulum • Lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled here. Rough ER makes proteins. • Both lipids and proteins are transported through the ER to the outside of the cell. Golgi apparatus • Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials from the ER. • Materials are either stored in the Golgi apparatus or secreted out of the cell. Lysosomes • Small organelles filled with enzymes • The enzymes break down large compounds such as lipids, carbohydrates and proteins. • The cell then reuses the smaller compounds to make new ones. Vacuoles & cytoplasm • Vacuoles store water, salt, proteins and carbohydrates • Vacuoles also serve as support structures in plants • The cytoplasm is the fluid that fills the cell in which all the other organelles float. Mitochondria • Mitochondria convert chemical energy stored in food into compounds the cell can use (ATP) • The ‘powerhouse’ of the cell • All our mitochondria come from our mothers. Chloroplasts • Found only in plant cells, cyanobacteria. • Photosynthesis, the process that converts solar energy to chemical energy, occurs here Cytoskeleton • A network of protein filaments that helps the cell keep its shape. • Also involved in cell movement. Can you name the organelles?