Cell Cycle PowerPoint
advertisement

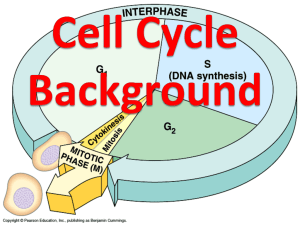
HAPPY MONDAY Bellwork: Quickwrite: In 26 words, describe how you think the body grows and develops on a cellular level? Collect Today Page 53 - Codon Face Project Assigned Page 56 – Interphase Handout (TOMORROW) Buff Binder Quiz #1 Makeup – (TOMORROW) T/T Quiz Makeup – (Wednesday) Late Page 51 – Protein Synthesis Worksheet (-50%) Page 52 – Transcription & Translation Practice Worksheet (-50%) Unit 4 – Cell Cycle Definitions Due Friday (11/6/15) All Parts Due Friday (11/13/15) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Allele Anaphase Cancer Cell Cycle Centriole Centromere Chromatid Chromosome Crossing Over Cytokinesis Daughter Cell 12. Diploid 13. Electrophoresis 14. Frameshift Mutation 15. Gamete 16. Gene 17. Genetic Disorder 18. Genome 19. Haploid 20. Interphase 21. Karyotype 22. Meiosis 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. Pg 54 Metaphase Mitosis Mutation Offspring Point Mutation Prophase Sexual Reproduction 30. Somatic 31. Telophase 32. Tumor Essential Question Pg 55 What are the steps of the cell cycle? Standard B.5A – Describe the stages of the Cell Cycle, including Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of an organism. In most cases, living things grow by producing more cells. The two main reasons that cells divide rather than continue to grow indefinitely are: 1) the larger a cell becomes, the more demands it places on its DNA. 2) the cell has more trouble moving enough nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane. The information that controls a cell’s function is stored in a molecule known as DNA. If a cell continued to grow larger without dividing, its DNA wouldn’t be able to serve the increasing needs of the growing cell. Food, oxygen, and water enter a cell through its cell membrane, and waste products leave in the same way. The rate at which the exchange of materials takes place across the cell membrane depends on the surface area of the cell. The rate at which food and oxygen are used up and waste products are produced depends on the cell’s volume. As a cell increases in size, the volume increases much more quickly than the surface area. This is a problem because if the cell gets too large, more difficult to get sufficient amounts of oxygen and nutrients in and waste products out. Before it becomes too large, a growing cell divides forming two “daughter” cells. This process is called cell division. Cell division solves the problem of information storage because each daughter cell gets one complete set of genetic information. Cell division solves the problem of surface-areato-volume-ratio by increasing surface area and decreasing volume. The cell cycle is the series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide. During the cell cycle, a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells. G1 Label This S G2 Interphase is divided into the G1, S, and G2 stages. About 80% of the cell’s life is spend in Interphase. During the G1 phase, cells increase in size and make new proteins and organelles. During the S phase, chromosomes (DNA) are replicated (copied). During the G2 phase, many of the organelles and molecules required for cell division are Assembled. When the events of the G2 phase are completed, the cell is ready to enter mitosis and begin the process of cell division. All cells do not move through the cell cycle at the same rate. Muscle cells and nerve cells do not divide once they have developed. Skin, digestive tract, and bone marrow cells divide rapidly throughout life. Essential Question Pg 56 What are the steps of the cell cycle? Standard B.5A – Describe the stages of the Cell Cycle, including Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of an organism. Collect Today Page 53 - Codon Face Project Assigned Page 56 – Interphase Handout (TOMORROW) Buff Binder Quiz #1 Makeup – (TOMORROW) T/T Quiz Makeup – (Wednesday) Late Page 51 – Protein Synthesis Worksheet (-50%) Page 52 – Transcription & Translation Practice Worksheet (-50%) Sage and Scribe Can you draw a picture of the cell cycle and label the parts of interphase? Think-Pair-Share: What are the steps of the cell cycle?