Cell Cycle Lab
advertisement

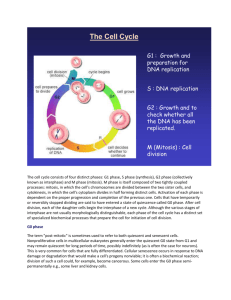
THE CELL CYCLE LAB Background Concurrent with the evolution of large cells containing a nucleus through endosymbiosis, a process of cellular and nuclear division had to develop. In unicellular organisms the cell division is a form of reproduction while in multicellular organisms it is a method of producing more cells during embryonic development or maintenance of cells in the adult organism. Objective 1) You should be able to use a compound light microscope with a prepared slide to observe and identify the phases of the cell cycle. Assignment 1. Answer the background question alone with your textbook, and be prepared to answer questions before being allowed to proceed to the lab activity portion of the activity. 2. Acquire a compound light microscope from the cabinets at the back of the room. 3. Acquire a prepared microscope slide of mitosis and focus on the slide under – power. 4. Next, scan the slide from left to right and from top to bottom searching for cells in the various stages of mitosis. As you find each stage of mitosis, call me over to check that you have found the correct phase and I will initial your class work for that phase in the space provided, after you have found the correct stage using the microscope and have describe the events of the stage in sentence form. THE CELL CYCLE LAB Name: _______________________________ Background Questions Questions (chapter 7 and 11) 1. What does the term diploid mean? 2. What cells in humans are diploid? How many chromosomes are found in the diploid cells of humans? 2. Describe the cellular processes occurring during the G1, S, and G2 stages of interphase. G1 – S– G2 – 3. DNA replication during the S phase of interphase is said to be “semiconservative”. What does this mean? 4. Identify and describe the function of enzymes critical to DNA replication (enzymes usually end in “ase”). Forms of DNA observed during the cell cycle. 1. Interphase _____ Description of the phase - 2. Prophase _____ Description of the phase - 3. Metaphase _____ Description of the phase - 4. Anaphase _____ Description of the phase - 5. Telophase _____ Description of the phase - 6. Cytokinesis _____ Description of the phase -