5.1 The Cell Cycle
advertisement
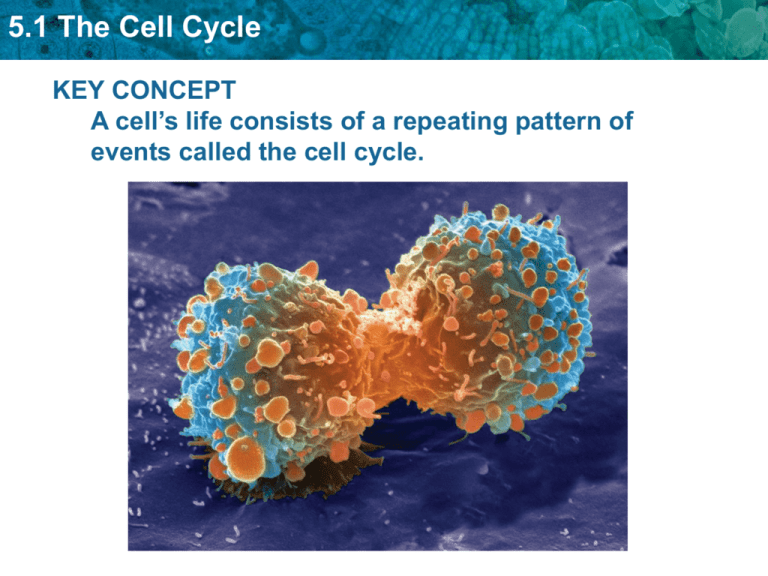
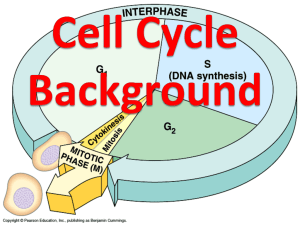
5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT A cell’s life consists of a repeating pattern of events called the cell cycle. 5.1 The Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Events include: • • • • Growth Carrying out is job DNA and organelle duplication Division 5.1 The Cell Cycle The Cell Cycle is divided into two main stages: Interphase and Cell Division . 5.1 The Cell Cycle INTERPHASE Purpose: Grow, Carry out Job, Prepare for Cell Division G1 - Cell growth, Do job Duplicate organelles S - DNA synthesis (copies DNA) G2 - Additional growth, Duplicate organelles Normal functions 5.1 The Cell Cycle 2 Parts of Cell Division “M” Stage: 1. Mitosis 2. Cytokinesis 5.1 The Cell Cycle MITOSIS “Nuclear Divison” Purpose: Divides nucleus into 2 genetically identical nuclei 4 Stages of Mitosis: • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase 5.1 The Cell Cycle CYTOKINESIS PURPOSE: Divide the cytoplasm to form two separate cells Animal Cell Plant Cell 5.1 The Cell Cycle The Final Product of the Cell Cycle…… • 2 Daughter Cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell – same # of chromosomes with same DNA information Start of Interphase End of Interphase/ Beginning of Mitosis End of Mitosis End of Cytokinesis 5.1 The Cell Cycle Reasons Cells Divide • • • • Growth Replacement Repair Maintain size limit (surface area to volume ratio) 5.1 The Cell Cycle Cell size is limited. • Volume increases faster than surface area. 5.1 The Cell Cycle Cells divide at different rates. • The rate of cell division varies with the need for those types of cells. • Some cells are unlikely to divide (G0) Ex. Neurons (nerves).