cardiac cycle ppt
advertisement
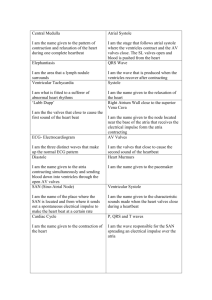
A complete heartbeat in which the heart chambers function in a coordinated fashion › Systole – heart chamber walls contract › Diastole- heart chamber walls relax Atrial systole (atria contracts) while ventricles relax called ventricular diastole Then the ventricles contract (ventricular systole) and atria relax (atrial diastole) Then the atria and ventricles both relax for an interval The cusps (flaps) of the bicuspid and tricuspid valves are anchored to the ventricle walls by fibrous “cords” called chordate tendineae, which attach to the wall by papillary muscles. This prevents the valves from being pushed up into the atria during ventricular systole Blood pressure rises in the ventricles, forcing the aortic and pulmonary valves(semilunar valves) open, while closing the tricuspid and bicuspid valves (A-V valves) This makes a lubb sound The pulmonary and aortic valves are closing, while the tricuspid and bicuspid valves open to let blood flow from the atria to the ventricles This makes a dubb sound http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/ 0072495855/student_view0/chapter22/a nimation__the_cardiac_cycle__quiz_1_.h tml The heart normally makes a lubb dubb sound. A heart murmur is a deviation from this sound and is usually due to a valve’s cusp not closing entirely, allowing blood to backflow from the ventricle into the atrium Ranges from harmless to requiring open heart surgery http://depts.washington.edu/physdx/he art/demo.html Stethoscope – instrument to listen and measure heart sounds Electrocardiogram- recording of the electrical charges that occur in the myocardium during a cardiac cycle › Electrodes are placed on the skin and respond to weak electrical changes P wave- atrial systole (contraction) › Review: What valves are closed and which are open? QRS complex- Ventricle systole (contraction) › Review: Which valves are closed and which are open? T wave- repolarization of the ventricles (resting period) Controlled by the cardiac center in the medulla oblongata Signals the heart to increase or decrease heart rate depending on various factors › Body temperature › Muscle activity › Blood Ca2+ & K+ levels Tachycardia = rapid heartbeat ( > 100 BPM) Bradycardia = slow heartbeat ( < 60 BPM) Fibrillation = rapid, uncoordinated unsynchronized heart rate. Atria (not serious. Ventricles (deadly) Common treatment for lifethreatening cardiac arrhythmia The device shocks the heart and allows it to re-establish its normal rhythm The device can also be used to start a heart that has stopped Device used to measure blood pressure Average normal blood pressure = 120/80 Average Heart Rate = 72 http://www.sumanasinc.com/webconte nt/animations/content/bloodpressure.ht ml