Meiosis 2
advertisement

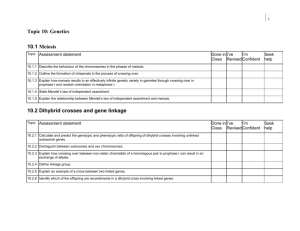
Think back to the first lesson on meiosis. List the order of the phases. Objectives • • • • • Describe the behaviour of the chromosomes in the phases of meiosis. Outline the formation of chiasmata in the process of crossing over. Explain how meiosis results in an effectively infinite genetic variety in gametes through crossing over in prophase I and random orientation in metaphase I. State Mendel’s law of independent assortment. Explain the relationship between Mendel’s law of independent assortment and meiosis. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. 5: Explain why there is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Key terms: chromosome, crossing over, chiasmata, Mendel. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. 5: Explain why the is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Key terms: chromosome, crossing over, chiasmata, Mendel. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. 5: Explain why the is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. 5: Explain why the is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Key terms: chromosome, crossing over, chiasmata, Mendel. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. 5: Explain why the is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Key terms: chromosome, crossing over, chiasmata, Mendel. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. Bivalent: when the homologous chromosomes have paired up closely. 5: Explain why the is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Key terms: chromosome, crossing over, chiasmata, Mendel. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. 5: Explain why the is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Key terms: chromosome, crossing over, chiasmata, Mendel. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. 5: Explain why the is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Key terms: chromosome, crossing over, chiasmata, Mendel. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. 5: Explain why the is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Key terms: chromosome, crossing over, chiasmata, Mendel. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. 5: Explain why the is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Key terms: chromosome, crossing over, chiasmata, Mendel. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. 5: Explain why the is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Key terms: chromosome, crossing over, chiasmata, Mendel. Outcomes 3: Describe how crossing over leads to variation. 5: Explain why the is so much variation as a result of meiosis. 7: Evaluate how Mendel's law of independent assortment applies to meiosis. Key terms: chromosome, crossing over, chiasmata, Mendel.