Earth as a System
advertisement

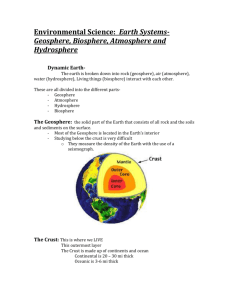
Earth as a System (Sect 1-2 & 1-4) Satellite image of ash cloud being spewed from fissure in Chile’s Puyehue-Cordón Caulle Volcanic Range, June 7, 2011 A. System • A system is an organized group of related objects or components that work independently and interact to create a whole. • Systems have matter and energy that flow freely through the system. • How matter and energy are transferred determines whether the system is closed or open. • A closed system is a system where only energy is transferred or exchanged with its surroundings. • Matter is not part of this exchange. A. System Example of a Closed System • Energy, in the form of light, can enter. • Energy can leave, too, as heat passes out through the glass walls of the jar. But if the jar is tipped over, the tea stays in. • As a closed system, the jar of tea does not share matter with its surroundings. A. System An open system includes the transfer and exchange of both matter and energy with the system's surroundings. An example of a open system: The jar of iced tea would become an open system if the lid of the jar were to be removed, allowing some of the tea to evaporate. If a lemon slice were added, new matter would enter the system. B. Earth’s Major Spheres Atmosphere Biosphere All Air, gases All Living Things Geosphere Hydrosphere All Rock material All Liquid/Frozen Water C. Atmosphere C. Atmosphere • Thin gaseous envelope that surrounds the Earth • Approximately 100 km above the Earth’s surface. The Atmosphere Provides: • Air we breath • Protection (solar heat and radiation) • Energy exchanged between space, atmosphere and Earth’s surface produce weather and climate. D. The Geosphere • Geosphere is divided into 3 main parts based on composition of material (Crust,Mantle Core): D. The Geosphere • Crust: – Continental (thicker less dense) – Oceanic (thinner, more dense) C. The Geosphere • Mantle: – Lithosphere = crust + uppermost rigid mantle – Asthenosphere = upper mantle that is softer, flows – Lower mantle = also called mesosphere D. The Geosphere • Core: made of iron and nickel – Outer core (liquid), causes magnetic field – Inner Core (solid): even though hotter, pressure too high for liquid state) D. The Geosphere • The surface of Earth is covered with plates: • Plate Tectonics: Theory (i.e., an explanation) as to why continents have moved and the occurrence of EQs and volcanic eruptions. • Constructive and destructive process E. Biosphere E. Biosphere • Includes all life on Earth • Extends from the ocean floor upward into the atmosphere. • Living things form ecological communities called biomes. • Examples of biomes include: • Deserts • Grasslands • Tropical Rainforests F. Hydrosphere F. Hydrosphere • All of the Earth’s water makes up the hydrosphere. • Water is continually moving • Evaporation • Precipitation • Running Water (i.e. streams and rivers) • Oceans account for 97% . • Fresh water accounts for 3% • Groundwater, streams, lakes and glaciers • Sustaining life • Creates Earths Features • Availability of fresh water determines where many organisms can live. F. Hydrosphere Atmosphere Biosphere Geosphere Hydrosphere •Spheres are interconnected and interdependent •Soil is an interface between all of these G. Earth as a System • The Sun (light) drives external processes that occur in atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere H. People and The Environment • Humans can alter the system as well. • Environmental Science: focuses on relationships between people and natural world. • Resources that society depends on are formed by natural processes on Earth – Water, soil, metal and nonmetal minerals (ores), and energy Sample from a zinc ore mine in Franklain, NJ H. People and The Environment Renewable Resources Nonrenewable Resources •Replenished over short •Replenished only over time VERY long time periods •Ex: plants/animals for because process to create is food, natural fibers, forest SLOW products for lumber and •Ex: Aluminum, Copper paper (though these can recycle) •Energy: flowing water, •Energy: fossil fuels like oil, wind, solar energy natural gas, coal H. People and The Environment Population •How long will supplies of basic resources last??? http://www.census.gov/main /www/popclock.html • As population increases, so does demand for resources. Especially as world societies become developed.