The Atmosphere
advertisement
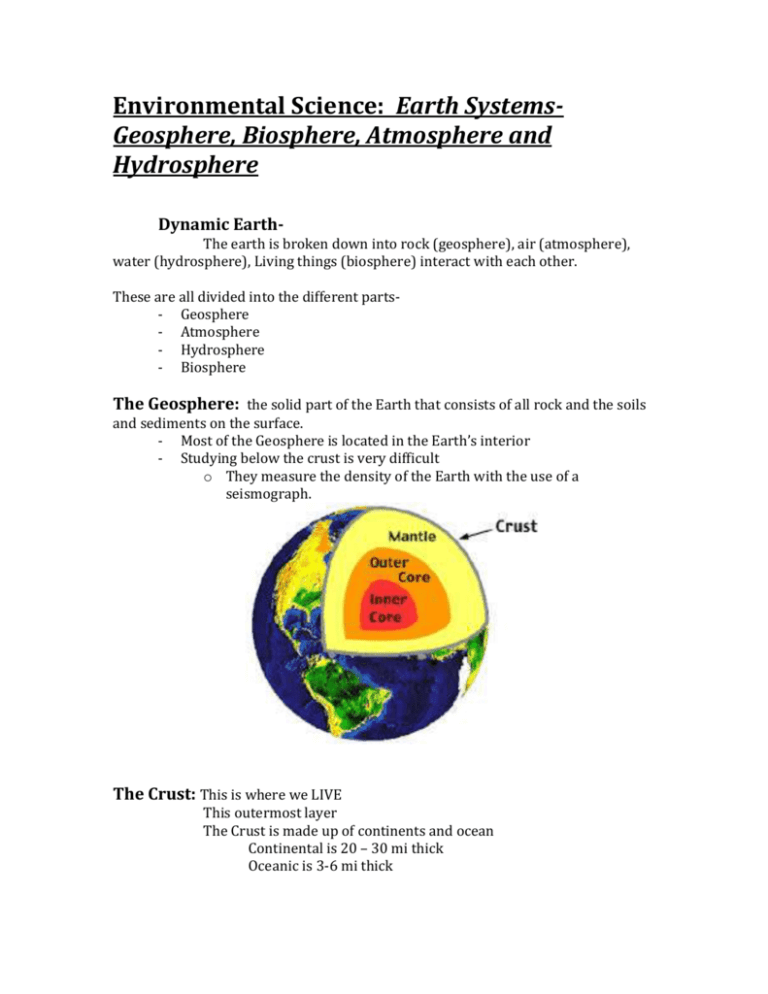
Environmental Science: Earth SystemsGeosphere, Biosphere, Atmosphere and Hydrosphere Dynamic EarthThe earth is broken down into rock (geosphere), air (atmosphere), water (hydrosphere), Living things (biosphere) interact with each other. These are all divided into the different parts- Geosphere - Atmosphere - Hydrosphere - Biosphere The Geosphere: the solid part of the Earth that consists of all rock and the soils and sediments on the surface. - Most of the Geosphere is located in the Earth’s interior - Studying below the crust is very difficult o They measure the density of the Earth with the use of a seismograph. The Crust: This is where we LIVE This outermost layer The Crust is made up of continents and ocean Continental is 20 – 30 mi thick Oceanic is 3-6 mi thick The Mantle: The layer found right under the crust 1800 miles thick 500- 4000 degrees celcius made up of rocks and it is not as light as the crust but not as dense of the core has a liquid layer that makes up the lava that erupts out of volcanoes. The Lithosphere: consists of the CRUST and the UPPER PART OF THE MANTLE - The Lithosphere is divided into large pieces of earth called: Tectonic Plates The Asthenosphere: This is the layer that is below the Lithosphere - It consists of the “plastic “ part of the mantle Rock flows smoothly like melted plastic Allowing the plates of Earth to move. Plate Movement: - Plates can either: o Pull apart or o Squeeze together or o Slip past each other Major geological activity caused can be -Volcano -Earthquake- faults -Mountains -Ocean Ridges Volcanoes: Mountain build from magma Volcanoes are usually found at plate boundaries Can occur on land or in the ocean Global Effects of Geological Events: Dust and Chemicals from volcanoes enter atmosphere Chemicals become part of runoff Global temperature decreases Erosion- Wearing down of rocks o Water o Wind The Atmosphere - Consists of a mixture of gases that surround earth Nitrogen, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide and other gases Gases are constantly added and removed from the atmosphere Insulates the Earth’s surface Composition of the Atmosphere: Nitrogen- 78% Oxygen- 21% Argon, Carbon Dioxide, Methane and Water Vapor- 1% Layers of the Atmosphere: The Troposphere- is the closest to the Earth’s surface. This is where weather occurs Temperature decreases as you move further into the Troposphere. Stratosphere: Is the layer above the Troposphere Temperature increases as you go further into the Stratosphere This happens because the ozone absorbs the sun’s UV light and warms the air (O Ozone 3) is a molecule made of 3 oxygen atoms Ozone layer limits the amount of UV light that reaches the Earth The Greenhouse Effect: - Sunlight heats the surface of the Earth The surface radiates the heat back to the atmosphere, where some heat escapes into space The rest of the heat is absorbed by greenhouse gasses which heats the air Heat then radiates back to the Earth Gasses trap the heat near the Earth- Greenhouse Effect The Hydrosphere: Includes all water on or near the Earths surface The Biosphere: - The narrow layer around Earth’s surface in which life can exist Consists of the upper most part of the Geosphere, most of the hydrosphere and the lower part of the atmosphere.