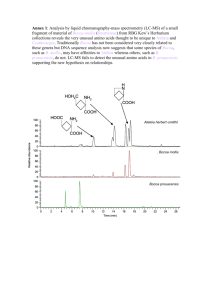
Feng Chen
advertisement

Progress Report for the 2010AtSABATH Group Meeting Feng Chen Ann Arbor, June 2004 1. Management 2. Progress and Resources on 5 Genes 3. High-throughput Biochemical Assays Part I: Report on Management Design and Construction of the Project Webpage NSF Arabidopsis 2010: Functional Analysis of the SABATH Family of Methyltransferases Project Summary The Arabidopsis thaliana genome contains 24 related genes that encode methyltransferase enzymes (MTs) distinct from any other known MTs. One MT from this group has been shown to convert jasmonic acid, an important plant hormone, into the jasmonate methyl ester, thereby changing the activity of the hormone in significant ways. Preliminary experiments suggest that the other 23 MTs of this group convert several important hormones and other plant constituents into the methyl esters, thereby exerting important effects on the biological activity of these molecules and consequently on a myriad of important physiological processes. The aim of the project is to identify the function of all the MTs of this group (i.e., which compound each of them methylates) by a combination of methods that involve genetics, enzymology, protein structure determination, and analytical chemistry. The consequences of the methylation of such hormonal molecules on the physiology of the plant will be examined in selected cases, which may include processes involving plant response to pathogens, drought conditions, and herbivory. The results are expected to provide a better understanding of plant responses to environmental conditions, thus helping improve crop yield and nutritional value. In addition, by developing methodologies for determining which Arabidopsis genes are involved in the synthesis of the plant’s diverse repetoire of small molecules, the project will contribute to the elucidation of the function of other Arabidopsis genes involved in hitherto unknown biochemical pathways. The project will also provide interdisciplinary opportunities for training undergraduates, graduates, and post-docs. Created by Feng Chen, fengc@umich.edu, last updated on January 26, 2004 Database Gateway Entry and Destination Vectors GW Entry Vectors TOPO pENTR/D-TOPO attL1 CCCTT GGGAAGTGG AAGGG TTCCC Knr attL2 TOPO ccdB pDONR207 Gentr CmR attP1 attP2 GW Destination Vectors for E.coli Expression ccdB T7 Promoter pH9GW RBS MK9His Knr CmR attR1 attR2 ccdB pH8GW T7 Promoter RBS Thrombin MK8His Knr CmR attR1 attR2 GW Destination Binary Vectors for Plant Over-expression pMDC32 RB ccdB 2X35S CmR pCHF3-GW1 35S RB CmR nptII T Specr LB attR2 ccdB 35S RB Knr LB attR2 ccdB attR1 pCHF3-GW3 Hygr Nos T attR1 CmR attR2 nptII T Specr LB attR1 GW Destination Binary Vectors for Reporter Assays ccdB pMDC162 CmR RB gus Nos T Hygr LB Knr gus Nos T nptII LB Gentr LB Gentr LB Knr attR2 attR1 ccdB pDW137-GW1 CmR RB attR1 attR2 ccdB pDW137-GW2 CmR RB attR2 gus Nos T nptII attR1 ccdB pMDC107 CmR RB attR1 gfp6his attR2 Nos T Hygr Material Archiving 1. DNA Construct Stocks 2. DNA Oligo Stocks 3. Transgenic Seed Stocks Part II: Resources and Progress on MT6, MT7, MT8 MT10 and MT19 Expression Analysis and cDNA Cloning 6 7 8 10 19 GUS reporter Analysis: MT7 GUS reporter Analysis: MT8 GUS reporter Analysis: MT10 T-DNA Knock-out Lines Gene Source Position of insertion Homozygou s lines MT6 SALK Intron X MT7 SALK 5’-UTR X Garlic Intron X GABI Exon X SALK Exon X SALK Intron X Garlic Exon X MT8 MT10 MT19 Plant Over-expressiors Gene Binary Construct Plant Transformation MT6 X X MT7 X X MT8 X X MT10 X X MT19 X X Transgenic Lines X Part III: High-throughput Biochemical Assays Phenolic Acids and Phenylpropanoids COOH COOH COOH COOH NH2 OH BA COOH COOH OH SA OH 3-OH BA 4-OH BA NH2 Anthranilic acid 4-amino BA COOH COOH COOH COOH COOH OH OMe OH OMe OH OH Caffeic acid OH P-coumaric acid Ferulic acid 3-hydroxy-4-methoxy Cinnamic acid Cinnamic acid COOH O COOH HO MeO HOOC HO OMe OMe O OH OH OH OH COOH O HO Rosmarinic acid Vanillic acid 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxy Cinnamic acid COOH COOH O HO OH HO COOH HO MeO HO OMe OH O OH chlorogenic acid COOH O Phenylpyruvic acid Gallic acid Shikimic acid COOH HO Chorismic aicd COOH O OH 4-hydroxy Phenylpyruvic acid COOH OH OMe Phenyllactic acid HO COOH OH 4-hydroxy Phenyllactic acid Phytohormones and Related Compounds OH H OH O O COOH H O H HO ABA N H COOH H GA Indole COOH COOH N H Cl N H O COOH Cl IAA IBA 2,4-D H3C H2 C CH2 C H2 OH N N H2 C HN HN HN O H2 C N HN N H N H N Kinetin COOH N HN N Zeatin HN O N H Jasmonic acid N6-benzyladenine O OH OH OH NH3 COOH CH2 O OH CH2 GABA (gama-amino butyric acid) O DOPA (3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine) OPDA Acidic Sugars, Pectin and Vitamin C HOOC HOOC O O HO HO OH HO OH HO OH Galacturonic acid Tri-galacturonic acid HOOC HOOC O O HO O HO OH OH HO OH HO O OH n pectin O HO HO OH Ascorbic acid Fatty Acids COOH HOOC norBixin Short-chain (2-4) fatty acids Butanoic acid (4:0) Medium-chain (6-10) fatty acids Pentanoic acid (5:0) Hexanoic acid (6:0) Octanoic acid (8:0) Decanoic acid (10:0) Long-chain (>12) fatty acids Lauric acid (12:0) Myristic acid (14:0) Palmitic acid (16:0) Stearic acid (18:0) Arachidic acid (20:0) Behenic acid (22:0) Lignoceric acid (24:0) Oleic acid (18:1) Petroseenic acid (18:1) a-Linoleic acid (18:2) r-linoleic acid (18:3) Roughanic acid (16:3) Erucic acid (22:1) Nitrogen-containing Compounds O O H N HN O N H N HN O NH Ribose O CH3 N H NH O 7-methyl-Xanthine O O H3C O N N N H CH3 N paraxanthine N HN O CH3 N N CH3 Theobromine N S NH3 C C COOH H2 H2 -alanine CH3 N N H Ribose 7-methylXanthosine Xanthosine N HN N H Camalexin Amino Acids COOH COOH COOH N H COOH H2N COOH H2N NH2 NH3 HO Tryptophan Phenylalanine H2N H CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 NH CH2 Tyrosine NH NH2 NH2 Lysine Arginine COOH COOH H2N H COOH COOH H2N CH3 H2N H CH2OH Alanine Serine H2N H H CH2 CH2 CH2 COOH COOH Aspartic acid Glutamic acid COOH COOH COOH H2N COOH H H2N H3C CH H CH3 H2N H H2N COOH H H2N HC CH3 C H3C H CH3 CH3 H2N COOH H CH2 OH CH2 CH3 Valine Threonine Leucine Isoleucine COOH H CH2 H2N CH2 CH2 O NH2 Glutamine H O COOH H2N H CH2H N CH2 CH2 S SH CH3 Cysteine Methionine NH2 COOH C H2C H NH C C H2 H2 N Asparagine Histidine Proline H CH2 H COOH H2N H COOH H2N H H Glycine Substrate Grouping (1 to 3) Benzoic acid Caffeic acid 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxy-cinnamic acid * Chlorogenic acid Phenylpyvuvic acid Group 1 (EtOH) Salicylic acid Ferulic acid Vanillic acid Gallic acid 4-hydroxy-phenylpyvuvic acid Group 2 (EtOH) 3-hydroxy-benzoic acid Anthranillic aicd p-coumaric acid Jasmonic acid Shikimic aicd Group 3 (EtOH) Substrate Grouping (4 to 6) 4-hydroxy-benzoic acid 4-amino benzoic acid Cinnamic acid 3-hydroxy-4-methoxy-cinnamic acid * Rosmarinic acid 4-hydroxy-phenyllactic acid ABA GA IAA IBA 2,4-D Indole Group 4 (EtOH) Group 5 (EtOH) Zeatin Kinetin 6-benzylaminopurice GABA * DOPA * Tryptophan Group 6 (DMSO) Substrate Grouping (7 to 10) Trigalacturonic acid Muranic acid Octanoic acid Decanoic acid Lauric acid Myristic acid Palmitic acid Stearic acid Xanthosine 7-methyl xanthine theobromine paraxanthine beta-alanine (Camalexin) Glutamic acid Valine Alanine Phenylalanine Aspartic acid Asparagine Group 7 (DMSO) Group 8 (EtOH:Chloroform=1:1) Group 9 (DMSO) Group 10 (H2O) MT7 showed activity with Lauric acid COOH Fully expended leaves of Col at growth stage 3.9 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 Plant Defense Response (I) 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 HrpA CTR 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 Plant Defense Response (II) 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 DC3000 avrRpm1 HrpA CTR 0 500 1000 1500 2000 250 Plant Defense Response (III) 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 DC3000 HrpA 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 COOH Lauric Acid COOH Traumatic Acid HOOC