ครั้งที่ 2
advertisement
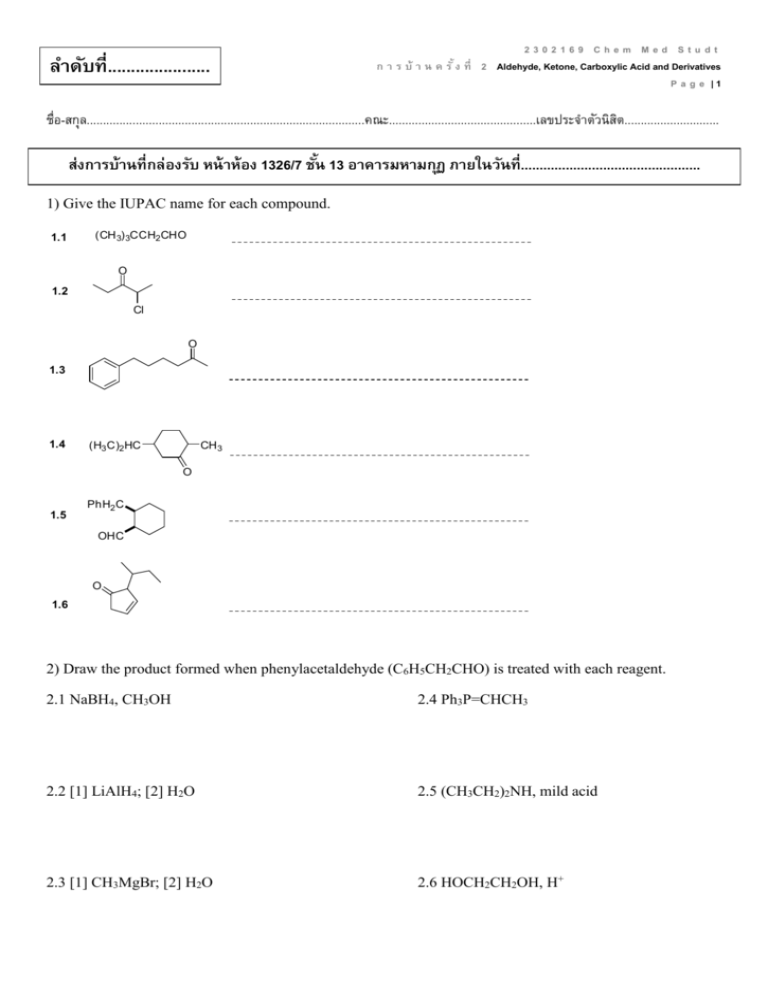
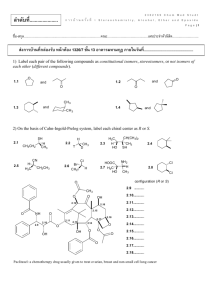
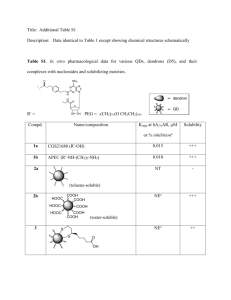
ลาดับที่...................... 2302169 Chem Med Studt ก า ร บ้ า น ค รั ้ ง ที่ 2 Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives P a g e |1 ชื่อ-สกุล.....................................................................................คณะ.............................................เลขประจำตัวนิสติ ............................. ส่งการบ้านที่กล่องรับ หน้ าห้อง 1326/7 ชัน้ 13 อาคารมหามกุฏ ภายในวันที่................................................ 1) Give the IUPAC name for each compound. 1.1 (CH 3) 3CCH2 CHO O 1.2 Cl O 1.3 1.4 (H3 C)2 HC CH 3 O 1.5 PhH2 C OHC O 1.6 2) Draw the product formed when phenylacetaldehyde (C6H5CH2CHO) is treated with each reagent. 2.1 NaBH4, CH3OH 2.4 Ph3P=CHCH3 2.2 [1] LiAlH4; [2] H2O 2.5 (CH3CH2)2NH, mild acid 2.3 [1] CH3MgBr; [2] H2O 2.6 HOCH2CH2OH, H+ 2302169 Chem Med Studt ก า ร บ้ า น ค รั ้ ง ที่ 2 Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives P a g e |2 3) Draw the products formed in each reaction sequence. 3.1 [1] Ph 3P CH 3CH2 Cl 3.2 [2] BuLi [3] (CH 3 )2 C=O CH 2Br CH 2 Cl 3.3 [1] Ph 3P [2] BuLi [3] C 6 H5 CH 2 CH 2CHO [1] Ph 3P [2] BuLi [3] CH 3CH2 CH2 CHO 4) Draw all stereoisomers formed in each reaction. 4.1 Ph3 PH=CHCH2 CH 2CH 3 butanal 4.2 2-butanone NaCN HCl 4.3 NaBH4 O CH 3OH CH2 CH 3 O 4.4 OH CH 3OH HCl OH 2302169 Chem Med Studt ก า ร บ้ า น ค รั ้ ง ที่ 2 Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives P a g e |3 5) Draw the products of each reaction. 5.1 CH 3CH 2CHO 5.2 O + H 2N mild acid HOCH 2CH 2OH H+ 5.3 H3 O+ N HO CN H3 O+ 5.4 heat 5.5 N H3 O+ 6) Show two different methods to carry out each transformation: a one-step method using a Wittig reagent and a two-step method using a Grignard reagent. 6.1 6.2 cyclohexanone cyclohexanecarbaldehyde 2302169 Chem Med Studt ก า ร บ้ า น ค รั ้ ง ที่ 2 Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives P a g e |4 7) Give an IUPAC name for each compound. 7.1 (CH 3) 2CHCH 2CH 2COOH 7.2 BrCH 2COOH O 7.3 OH 7.4 CH 3CH 2CH2 COO- Li+ 7.5 H 3CH2 C 7.6 COOH COOH 8) Draw the organic products formed in each reaction. CrO3 OH 8.1 H2 SO4 , H2 O 8.2 (CH 3) 2CH CH 3 8.3 CH 3(CH 2) 6CH 2OH KMnO4 Na 2Cr 2O7 H2 SO4 , H2 O 9) Rank the compounds in each group in order of increasing acidity. Cl 9.1 Br COOH COOH b a COOH 9.2 H3 C COOH c COOH COOH F3 C a b c 2302169 Chem Med Studt ก า ร บ้ า น ค รั ้ ง ที่ 2 Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives P a g e |5 10) Give an IUPAC name for each compound. 10.1 (CH3 )3 CCOCl O 10.2 O 10.3 (CH3 )3 CCOOCH 2CH(CH3 )2 O O O 10.4 COCl 10.5 Br 10.6 NHCOC 6 H5 11) Rank the compounds in each group in order of increasing reactivity in nucleophilic acyl substitution. 11.1 CH3 CH2 CH 2CONH 2 a 11.2 11.3 CH3 CH2 CH 2COCl b CH3 CH2 CH 2COOCH 2CH 2CH3 c (CH3 CH2 CO)2 O (CF3CO) 2O a b c CH 3COOH CH 3COSH CH 3COCl c a b CH3 CH2 CO 2CH2 CH2 CH 3 12) Draw the product formed when pentanoyl chloride (CH3CH2CH2CH2COCl) is treated with each reagent. 12.1 H2O, pyridine 12.4 NH3 (excess) 12.2 ethanol, pyridine 12.5 (CH3CH2)2NH (excess) 12.3 CH3COO- 12.6 C6H5NH2 (excess) 2302169 Chem Med Studt ก า ร บ้ า น ค รั ้ ง ที่ 2 Aldehyde, Ketone, Carboxylic Acid and Derivatives P a g e |6 13) Draw the product formed when pentanoic anhydride [(CH3CH2CH2CH2CO)2O] is treated with each reagent. With some reagents, no reaction occurs. 13.1 SOCl2 13.4 NaCl 13.2 H2O 13.5 (CH3CH2)2NH (excess) 13.3 methanol 13.6 CH3CH2NH2 (excess) 14) Devise a synthesis of each compound using 1-bromobutane (CH3CH2CH2CH2Br) as the only organic starting material. You may use any other inorganic reagents. H N 14.1 O O 14.2 O 14.3 O