Articulations
advertisement

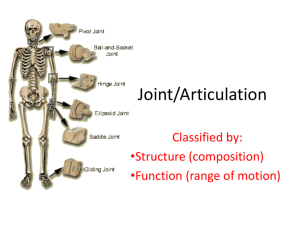
Articulations Articulations- points where two or more bones come together to form a joint [ maybe rigid or movable] Classified by Structure or Function • Structure- based on material that joins bones together Fibrous – fibrous connective tissue Cartilagenous – hyaline or fibrocartilage Synovial – joint cavity with synovial membrane Synovial Joint Capsule is continuous with periosteum Membrane is 2 layers Has blood vessels & nerves Synovial Fluid • Continuously made, circulated – at any time there is 3 ml [ 0.1 oz] in cavity • Resembles interstitial fluid, but contains proteoglycans secreted by fibroblasts making it thick / viscous • Functions: lubricate joint distribute nutrients and remove waste products shock absorber defense Accessories of Synovial Joint • Cartilage – fibrocartilage [articular discs or meniscus] • Fat – articular fat pads • Ligaments [ attach bone to bone] • Tendons [ attach muscle to bone] • Bursae – synovial fluid filled ‘pockets’ mini shock absorbers • Function – based on degree of movement Synarthroses – immovable Amphiarthroses – slightly movable Diarthroses – freely moveable Fibrous Articulations • Bones are held tightly connected by fibrous connective tissue or cartilage. Joints are rigid and immoveable. Sutures – found only in skull. Bones joined by fibrous connective tissue Syndesmosis – band of fibrous connective tissue, holds bones tightly together distal end of tibia/fibula Gomphosis – peg in socket tooth in alveoli- periodontal ligament Syndesmosis Cartilagenous Articulations Hyaline or fibrous cartilage joins bones; limited motion in response to twisting, compression, stress Synchondrosis – hyaline cartilage joins bones. epiphyseal plate, costal cartilages Symphysis – pad of fibrocartilage separates bones. intervertebral discs, symphysis pubis Synchondrosis Symphysis Synovial Articulations • Freely moveable joints. Include a capsule lined with a membrane and contains fluid Range of movement limited by: 1. Structure of bones 2. Strength and tautness of ligaments, tendons, joint capsule 3. Size, arrangement, action of muscles Types of Synovial Articulations • Hinge – concave surface on one articulates with convex surface of another. • Pivot – conical surface on one articulates with depression on another • Condyloid – oval condyle on one articulates with elliptical cavity on another • Gliding- flattened or slightly curved articulating surfaces • Saddle – concave and convex surface on each articulating bone • Ball and Socket – rounded surface on one articulates with cuplike socket on another Pivot saddle Ball & Socket Condyloid Gliding Hinge •Bursa – fluid filled sacs near diarthrotic joints – between muscles, skin and bones or tendon and bone. Reduce friction and stress associated with movement •Tendon Sheaths – modified bursae that surround and lubricate tendons of certain muscles, esp. those that cross wrist and ankle