Chordata - Raleigh Charter High School
advertisement

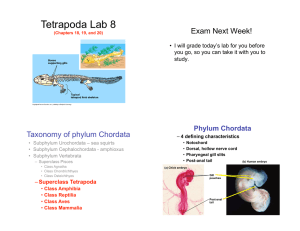
Chordata 6th Period Ashley Rouse Kenneth Saunders Saourya Marivada Charateristics of Chordata • Notochord- a stiff rod that helps support the dorsal nerve cord and body of the organism • Pharyngeal Slits- an opening from the neck to the throat that helps separate food from water and helps with gas exchange • Dorsal Nerve Chord- lateral muscles/organs gets messages from the brain from the nerve fibers that are attached to the brain • Post-anal Tail- helps organism swim, tail goes past the anus Urochordata (adult) Incurrent Siphon • Incurrent siphonwater enters • Pharynx- water is filtered • Stomach- receives food from the water • Excurrent Siphonsquirts out water Excurrent Siphon Pharynx Stomach Urochordata (larva) • Has: – Notochord – Dorsal, hollow nerve cord – Post- anal tail • This makes them part of the phylum chordata Cephalochordata (lancelets) • Swim thru the water using notochord muscles • Each muscle segment is called a somite Vertebrata • 7 Classes: – – – – – – – Agnatha Chondrichthyes Osteichthyes Amphibia Reptilia Aves Mammalia Agnatha • Greek- “no jaws” • lampreys and hagfish • Characteristics: – No paired appendages (fins) – Some attach to host and feed off of host’s blood – Some eat dead fish or marine worms Chondrichthyes • Chondr= Cartilage; -ichthyes= fish • Have a jaw and paired appendages (fins) • Subclasses: – Elasmobranchii (sharks, rays) – Chimaera (chimaeras) • Lateral line system- detects vibrations in the water Chondrichtyes Osteichthyes • Oste= Bone; ichthyes= fish • Bone endoskeleton made with hard calcium phosphate • Operculum- protective flap over the gills • Swim bladder- sac filled with gas that controls the buoyancy of the fish • Have better control in swimming than sharks Osteichthyes Amphibia • First vertebrates on land (salamanders, frogs, caecilians) • Fins evolved into legs • “Double Life” – Egg in water – Mature life on land • Cold-blooded • Urodeles (salamander) – “tailed ones” • Anurans (frogs, toads) – “tail-less ones” – Metamorphosis- tadpole to frog • Apodans (caecilians) – “legless ones” – Live in tropical areas and burrow into soil Amphibia Reptilia • Amniotic egg allowed reptiles to reproduce without dependence on water • Lizards, snakes, turtles, and crocodiles • Use solar energy to control body temp (ectotherm) • Adaptations for land – Scales with keratin – Obtain all oxygen with lungs – Can lay amniotic eggs on land Reptilia Aves • Evolved from reptiles • Archaeopteryx- earliest bird (Jurassic Period) • Bird anatomy enhances flight – Hollow bones – Females have one ovary (reduces weight) – Have larger brain than reptile – Very acute vision • Endothermic (maintain own body temp) • 4 chambered heart supports high metabolism • Ratites- flightless birds • Carinates- birds that fly Aves Mammalia • Endothermic • Have hair and fat layer to maintain heat • Mothers have mammary glands to nourish babies • Embryo usually grows in uterus instead of egg • Monotremes – Mammals with eggs – platypuses • Marsupials – Mammals with pouches – Kangaroos • Eutherian Mammals – Placental mammals – humans Mammalia Quiz Time!! Name That Subphylum!! Cephalochordata (lancelets) Urochordata Name the Class of Vertebrata Osteichthyes Amphibia Aves Chondrichthyes Reptilia Mammalia Agnatha