Document
advertisement

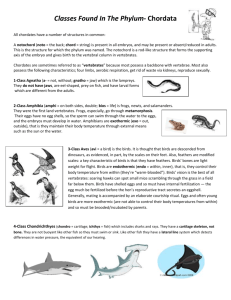
A. Characteristics of Chordata Notochord- a stiff rod that helps support the dorsal nerve cord and body of the organism Pharyngeal Slits- an opening from the neck to the throat that helps separate food from water and helps with gas exchange Dorsal Nerve Chord- lateral muscles/organs gets messages from the brain from the nerve fibers that are attached to the brain Post-anal Tail- helps organism swim, tail goes past the anus B. Urochordata (adult) Incurrent siphon- water enters Pharynx- water is filtered Stomach- receives food from the water Excurrent Siphon- squirts out water C. Urochordata (larva) Has: o Notochord o Dorsal, hollow nerve cord o Post- anal tail This makes them part of the phylum chordata D. Cephalochordata (lancelets) Swim thru the water using notochord muscles Each muscle segment is called a somite E. Vertebrata 1. Agnatha Greek- “no jaws” lampreys and hagfish Characteristics: o No paired appendages (fins) o Some attach to host and feed off of host’s blood o Some eat dead fish or marine worms 2. Chondrichthyes Chondr= Cartilage; -ichthyes= fish Have a jaw and paired appendages (fins) Subclasses: o Elasmobranchii (sharks, rays) o Chimaera (chimaeras) Lateral line system- detects vibrations in the water 3. Osteichthyes Oste= Bone; ichthyes= fish Bone endoskeleton made with hard calcium phosphate Operculum- protective flap over the gills Swim bladder- sac filled with gas that controls the buoyancy of the fish Have better control in swimming than sharks 4. Amphibia First vertebrates on land (salamanders, frogs, caecilians) Fins evolved into legs “Double Life” o Egg in water o Mature life on land Cold-blooded Urodeles (salamander) o “tailed ones” Anurans (frogs, toads) o “tail-less ones” o Metamorphosis- tadpole to frog Apodans (caecilians) o “legless ones” o Live in tropical areas and burrow into soil 5. Reptilia Amniotic egg allowed reptiles to reproduce without dependence on water Lizards, snakes, turtles, and crocodiles Use solar energy to control body temp (ectotherm) Adaptations for land o Scales with keratin o Obtain all oxygen with lungs o Can lay amniotic eggs on land 6. Aves Evolved from reptiles Archaeopteryx- earliest bird (Jurassic Period) Bird anatomy enhances flight o Hollow bones o Females have one ovary (reduces weight) o Have larger brain than reptile o Very acute vision Endothermic (maintain own body temp) 4 chambered heart supports high metabolism Ratites- flightless birds Carinates- birds that fly 7. Mammalia o Endothermic o Have hair and fat layer to maintain heat o Mothers have mammary glands to nourish babies o Embryo usually grows in uterus instead of egg o Monotremes o Mammals with eggs o platypuses o Marsupials o Mammals with pouches o Eutherian Mammals o Placental mammals