Tetrapoda Lab 8 Exam Next Week! Taxonomy of phylum Chordata Phylum Chordata
advertisement

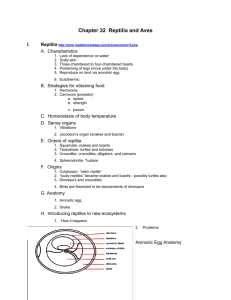
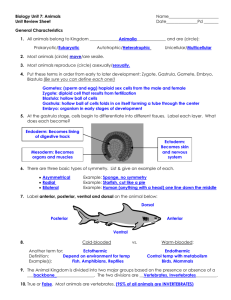
Tetrapoda Lab 8 Exam Next Week! (Chapters 18, 19, and 20) •! I will grade today’s lab for you before you go, so you can take it with you to study. Taxonomy of phylum Chordata •! Subphylum Urochordata – sea squirts •! Subphylum Cephalochordata - amphioxus •! Subphylum Vertebrata –! Superclass Pisces •! Class Agnatha •! Class Chondrichthyes •! Class Osteichthyes –!Superclass Tetrapoda •! Class Amphibia •! Class Reptilia •! Class Aves •! Class Mammalia Phylum Chordata –! 4 defining characteristics •! Notochord •! Dorsal, hollow nerve cord •! Pharyngeal gill slits •! Post-anal tail (a) Chick embryo Gill pouches Post-anal tail (b) Human embryo Amphibia: salamanders and newts, frogs and toads, and caecilians Jaw Bones Legs Amniotic egg Milk / Fur Feathers Class: Amphibia Amphibia •! Ectothermic - can’t heat itself •! Still tied to water •! 3-chambered heart •! Tetrapod legs to side of body Colostethus Class: Amphibia Class: Amphibia Frog external anatomy (no scales; naked) •! Know the difference between a frog and a toad (parotoid gland) Tympanic membrane •! Cross-section slide (skin): epidermis, dermis, mucous glands, poison glands American toad www.wickersham.us/anne/frog.htm Class: Amphibia •!Frog larva Tadpole Bull Frog Class: Reptilia Turtles, Tortoises, Lizards, Snakes, Crocodiles, Alligators, Tuatara Class: Reptilia •! Ectothermic (except shivering pythons) Class: Reptilia •! No longer tied to water (amniotic egg) •! 3-chambered heart (4 in Croc and some monitor lizards) •! Tetrapod legs to side of body Class: Reptilia (amniotic egg) Reptile scales Epidermal in origin Fish skin Reptile scales Reptile scales •! For keying, look in the center of the back •! Turtle - Class: Reptilia Know the carapace (dorsal) and plastron (ventral) Scale type: Bony Dermal Plates Bony Dermal Plates •! Turtle - Class: Reptilia Know the carapace (dorsal) and plastron (ventral) Scale type: Bony Dermal Plates male's plastron is concave female's plastron is flat Class: Amphibia & Reptilia Keying: •! Use the dichotomous keys to determine the taxonomy of the amphibian and reptile specimens in lab. Characteristics for Keys Cloacal opening Longitudinal Slit Characteristics for Keys Pupil of eye Pupil Vertical Pupil not Vertical Transverse Slit Characteristics for Keys PIT between eye and nostril Characteristics for Keys Characteristics for Keys Parasphenoid (or vomerine) teeth Tongue bicornuate behind Roof of mouth Tongue attached in the front Class: Aves (birds) Class: Aves •! Endothermic •! Feathers (modified scales) •! Flight (some exceptions) •! Hollow bones (why?) •! Crop and Gizzard (no teeth) •! 4-chambered heart •! Amniotic egg Class: Aves (birds) Bird feathers Types: Down, filoplume, contour warmth Class: Aves (birds) Bird feathers Contour (flight) Feather Construction: Quill (Calamus), Shaft (Rachis) Flight Decoration Class: Aves (birds) Bird feathers Contour (flight) Feather Construction: Barbs, Barbules Class: Aves (birds) Bird beaks and feet: Maxilla (upper bill) Mandible (lower bill) Class: Mammalia •! Endothermic There are three major groups of mammals 1.! Monotremes - the egg-laying mammals. •! Hair (insulates the body) •! Mammary glands, (produce milk; nourish young) •! 4-chambered heart echidna 2.! Marsupials - the so-called pouched mammals (short gestation period) Example: kangaroos, wallabies Platypus with pups 3.! Placentals - most mammals –! Have a relatively long gestation period –! Complete embryonic development occurs within the mother Figure 18.22C Amniota: Anapsida: turtles and tortoises Diapsida:snakes, lizards, crocodiles, alligators, birds Synapsida: mammals Jaw Bones Legs Amniotic egg Milk / Fur Feathers