Day 112 - upwardsapbio
advertisement

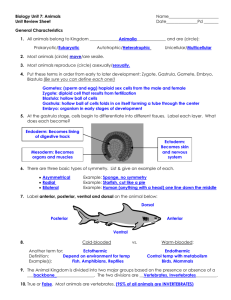
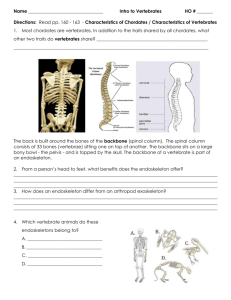
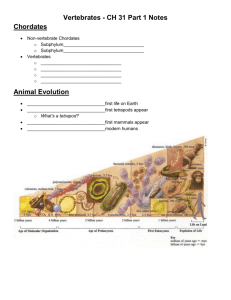
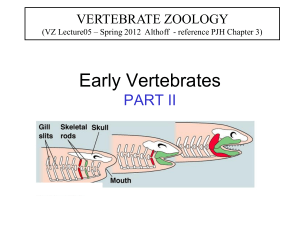
“Vertebrate Diversity /Phylogenetic Tree” phylogenetic tree A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or "tree" showing the inferred evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical and/or genetic characteristics. The taxa joined together in the tree are implied to have descended from a common ancestor. http://viwephotos.info/%E2%98%86%E2%98%86/phylogenetictree<<image . Trees are useful in fields of biology such as bioinformatics, systematics and comparative phylogenetics. Vertebrates Veryebrates- an animal of a large group distinguished by the possession of a backbone or spinal column, including mammals, birds, reptiles, General characteristics of vertebrates Vertebrates may be characterized by 12 general derived characteristics. You should become very familiar with these traits, and identify how they are expressed in the vertebrates you will see in lab. 1. Bilateral symmetry 2. Two pairs of jointed locomotor appendages, which can include fins (pectoral and anal/dorsal fins, as well as the forelimbs and hindlimbs). 3. Outer covering of protective cellular skin, which can be modified into special structures such as scales, hair and feathers 4. Metamerism found in skeletal, muscular and nervous system. This was described in a previous lecture - structures can include ribs, vertebrae, muscles and ganglia/peripheral nerves. 5. Well-developed coelom, or body cavity completely lined with epithelium (cellular tissue), that may be divided into 2 to 4 compartments. 6. Well-developed internal skeleton of cartilage and bone, separated into axial skeleton (skull, vertebrae, ribs, sternum) and appendicular skeleton (girdles and appendages). 7. Highly developed brain enclosed by skull, and nerve cord enclosed by vertebrae. This provides advanced neural structures that are highly protected from damage. 8. Well-developed sense organs (eyes, ears, nostrils) located on the head (cephalization). 9. Respiratory system, including either gills or lungs, and located closely to the pharynx or throat. 10. Closed circulatory system with ventral heart and median dorsal artery. 11. Genital and excretory systems closely related, utilizing common ducts and pathways. 12. Digestive tracts with two major digestive glands (liver and pancreas) that secrete into it. Grouping the vertebrate classes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. In the vertebrate classes, there are further ways of subdividing the groups based on derived characteristics. There are eight recognized extant classes of vertebrates Myxini– hagfishes Cephalaspidomorpha– lampreys Chondrichthyes - cartilagenous fishes Osteichthyes - bony fishes Amphibia - frogs, toads, salamanders, and caecilians Reptilia - turtles, snakes, lizards, crocodilians Aves – birds Mammalia - mammals Requirements in grouping Vertebrates Vertebrates can also be grouped based on their general habitat requirements: Pisces - collective term for all fishes; includes Myxini, Cephalaspidomorpha, Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes Tetrapoda - collective term for the terrestrial vertebrates; they have four feet unless some have been secondarily lost or converted to other uses. Includes Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, Mammalia Or based on their feeding habits: Agnatha - jawless vertebrates, including Myxini and Cephalaspidomorpha Gnathostomes - vertebrates with jaws derived from the mandibular arch, which may have (in primitive vertebrates) supported gills. Includes Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes, Amphibia, Reptilia, Aves, Mammalia Or based on their embryonic characteristics Anamniotes - vertebrates that lack an amnion, or extraembryonic membrane that surrounds the embryo and encases it in amniotic fluid. Includes Myxini, Cephalaspidomorpha, Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes, Amphibia. Amniotes - vertebrates that possess an amnion. Includes Reptilia, Aves, Mammalia http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xwuhmMIIspo<<video QUESTIONS: 1. What are three characteristic of vertebrates? 2. What are eight recognized extant classes of vertebrates? 3. What is a phylogenetic tree? 4. What is a vertebrate? 5. The taxa joined together in the tree are implied to have descended from a common________. a. reptiles b. ancestors c. insulin d. cell membrane ANSWERS: 1. Bilateral symmetry Two pairs of jointed locomotor appendages, which can include fins (pectoral and anal/dorsal fins, as well as the forelimbs and hindlimbs). Outer covering of protective cellular skin, which can be modified into special structures such as scales, hair and feathers 2. * Myxini – hagfishes * Cephalaspidomorpha – lampreys * Chondrichthyes - cartilagenous fishes * Osteichthyes - bony fishes * Amphibia - frogs, toads, salamanders, and caecilians * Reptilia - turtles, snakes, lizards, crocodilians * Aves – birds * Mammalia – mammals 3. A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or "tree" showing the inferred evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical and/or genetic characteristics 4. A vertebrate is an animal of a large group distinguished by the possession of a backbone or spinal column, including mammals, birds, reptiles, 5. b. ancestors