Ch-25-29-33-Animals-Study-Guide-Answers-1
advertisement

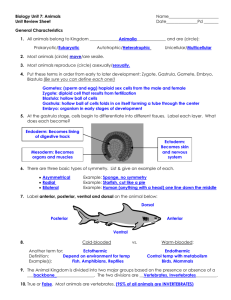
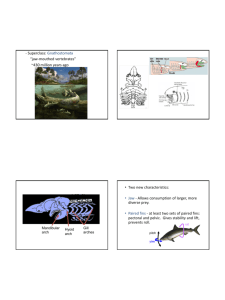
Bellringer • 5 minutes to finish your study guide • We will go over the answers together in class. Ch 25-29 & 33 Animals Study Guide Answers!!! Vocab • Amniotic egg: reproductive organ surrounded by amniotic fluid and membranes for protection • Cephalization: concentration of sensory/brain structures at the front of the body • Dioecious: havign two distinct genders • Endotherm: warm-blooded; stable internal temp • Ectotherm: cold-blooded; controlled by environment • Hermaphrodite: having both male and female reproductive organs Vocab Cont’d • Mandibles: mouth parts used for holding, chewing, biting, sucking • Metamorphosis: changes in shape and body during development • Molting: shedding exoskeleton and forming a new one • Nematocyst: stinging cells • Sessile: fixed to one place • Spicules: tiny hard particles that make up the skeleton 1. List the 6 Characteristics that all animals have. -Multicellular, Eukaryotic, Heterotrophic, Have to digest food, Lack cell walls, Ability to move 2. Draw a four legged animal—label the four anatomical directions—anterior/ventral, posterior/dorsal, superior and inferior. • Dorsal/Posterior—towards the back • Ventral/Anterior—towards the front • Superior—towards the head • Inferior—towards the bottom 3. Explain the three types of symmetry and name one animal with each. Radial- body can be cut through any plane and be exactly alike (Ex: Starfish) Bilateral – body can be cut in two with both halves being exactly alike. (Ex: Humans) Asymmetry--body with an irregular shape (ExSponges) 4. Explain the 2 types of digestive systems (complete vs. incomplete) and name one animal with each Incomplete digestive system: one opening; food and waste enter and exit from the same opening Complete digestive system: two openings; food enters the mouth and wastes exit the anus 5. Explain the 2 types of circulatory systems (closed vs. open). Open circulation—fluid pumped from vessels into body cavity, then returned to vessels (Ex. arthropods and most mollusks) Closed circulation-- fluid stays in vessels (Ex. some mollusks, higher invertebrates, and all vertebrates) 6. Explain the 2 types of fertilization—number of eggs for each??? (internal vs. external) External fertilization- egg and sperm are released into the water; large numbers of eggs Internal fertilization- eggs are fertilized by sperm inside the mother’s body; fewer numbers of eggs 7. Which vertebrates are ectothermic? Which are endothermic? • Ectothermic—Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes, Amphibia, Reptilia • Endothermic—Aves, Mammals 8. What class of invertebrates will sting you? --Cnidarians 9. How many legs do insects have? How many legs do arachnids have? --Insects: 6 --Arachnids: 8 10. What does the name “Echinodermata” mean? “Chondrichthyes”? “Osteichthyes”? “Amphibian”? Name one animal in each group. • Echinodermata—”spiny skinned”—starfish • Chondrichthyes—”cartilage fish”—shark • Osteichthyes—”Bone fish”—catfish • Amphibia—”double life”—frog 11. List the 5 Characteristics that all Chordates have. 1. *Have a dorsal notochord, that becomes the spine. 2. An endoskeleton made of cartilage or bone. 3. Pharyngeal slits or gill pouches during development. 4. A dorsal nerve cord. 5. Post-anal tail 12. List the 6 classes of Vertebrates and two animals that belong to each. Then list two traits about each class (appearance mostly) - Chondrichthyes: (sharks/rays)--have fins and scales, breathe with gills. - Osteichthyes: (salmon/perch)--have fins and scales, breathe with gills. - Amphibia: (frogs/salamanders)--smooth, moist skin, no claws or scales - Reptilia: (snakes/lizards)--body covered w/scales or plates, have lungs/scales & plates/claws - Aves: (robin/ostrich)-- have wings and feathers, parents incubate eggs - Mammals: (whales/humans)-- have hair & mammary glands, have a diaphragm 13. What is unique about a monotreme mammal? A marsupial mammal? Name an animal of each group. • Monoteme—only mammals that lay eggs (platypus) • Marsupial—carry their young in a pouch (kangeroo) 14. What makes an animal a vertebrate? An invertebrate? Vertebrate = backbone Invertebrate = no backbone 15. Copy the following prompts. Then name the vertebrate class that was the first in the evolutionary sequence to have each trait. a. Three chambered heart = Amphibia b. Internal fertilization = Reptilia c. Use of an amniotic egg = Reptilia d. Warm-blooded = Aves e. Four chambered heart = Aves f. Birth to live young = Mammals