Sensation Perception
advertisement

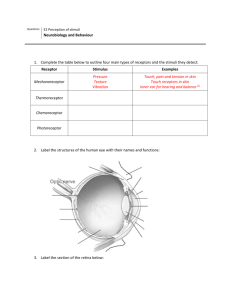
Sensation How we receive and represent stimulus information Perception Process of organizing and interpreting stimuli Bottom Up Processing Begins with sense receptors and then to the brain Top Down Processing Info processing guided by higher mental processes Psychophysics The study of the relationship between the physical characteristics of stimuli, such as intensity, and our psychological experience with them Absolute Threshold Minimum stimulation needed to detect a stimulus Signal Detection Theory A theory predicting how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus amid background noise. Assumes there is no universal absolute threshold Subliminal Difference Threshold Weber’s Law Sensory Adaptation Below threshold The minimum difference between 2 stimuli required for detection 50% of the time Stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage ( light = 8% difference) Diminished sensitively due to constant stimulation Transduction Wavelength Hue Cornea Conversion of one form of energy to another The distance from the peak of 1 light or sound wave to the next The dimension of color determined by the wavelength The part of the eye light enters through Bipolar Cells Cells that activate the ganglion cells Ganglion Cells The axons that forms the optic nerve Thalamus Sensory input station, all senses except smell Visual Cortex Area in the Occipital lobe the processes vision Occipital lobe Area of the brain that houses the visual cortex Intensity The amount of energy in a light or sound wave. Brightness or loudness Pupil Part of the eye that regulates the amount of the light that comes in Iris Colored part of the eye that controls the opening of the pupil Lens Part of the eye that changes shape to help focus images on the retina accommodation The process by which the eye’s lens changes shape to help focus images on the retina retina Part of the eye that houses the rods and cones acuity The sharpness of vision nearsightedness Seeing nearby objects better farsightedness Seeing faraway objects better rods Retinal receptors that detect black, white and gray. Don’t need a lot of light cones Retinal receptors that detect color. need a lot of light Blind spot Fovea Optic Nerve Area of the eye where the optic nerve leaves the eye The central focal point of the retina. Where the sharpest vision is found. Where the cones are clustered The nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain Feature Detectors Nerve cells in the brain that respond to specific features of the stimulus, such as shape, angle or movement Parallel Processing The processing of several aspects of a problem at once. ( shape, color, size..) Young Helmholtz Trichromatic The theory that the retina contains 3 different color receptors ( red, green, blue). Mixing paint Opponent Process Theory The theory that opposing (opposite) retinal processes enables color vision. Red-green, yellow-blue, black-white Color Constancy Perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color, even if changing illumination alters the wavelengths Audition Frequency Pitch Middle Ear Inner Ear Cochlea Outer Ear Hearing The number of complete wavelengths that pass a point A tone’s highness or lowness. Depends on frequency Part of the ear that contains the hammer, anvil and stirrup. Goal is to continue the vibration Part of the ear that contains the cochlea, semicircular canals and vestibular sacs Part of the inner ear that contains the cells Part of the ear that includes the ear flap, auditory canal and eardrum Eardrum Ossicles Hair Cells Also called the tympanum. Creates a vibration Anvil, stirrup and hammer. Continues the vibration Located in the cochlea. Transduce the vibrations into a neural impulse Basilar Membrane The area inside the cochlea that contains the hair cells Auditory Cortex Area of the temporal lobe that processes hearing. Temporal Lobe Area of the brain that houses the auditory cortex Auditory Nerve Transmits sounds from the ear to the brain Hemholtzs Place Theory Theory that different pitches stimulate different areas on the cochlea Frequency Theory Theory that pitch is heard because the cochlea and sound waves vibrate at the same rate Volley Principle The idea that in order to obtain higher pitch levels neurons must alternate in their firing b/c each neuron can only fire 1000 times per second Conduction Hearing Loss Hearing loss due to mechanical system damage. A part is broken Sensorineural Hearing Loss Gate Control Theory Olfactory Bulbs Hearing loss due to damage to the nerve cells The spinal cord blocks or send pain signals to the brain Registers the sense of smell Sensory restriction People who are missing one or more of the 5 senses. Typically have heightened other senses Sensory Interaction The principle that one sense may influence another. Smell and the taste of food Kinesthesis The system of sensing the position and movement of individual body parts Vestibular Sense The sense of body movement and position, including the sense of balance Selective Attention Visual Capture Gestalt Figure Ground The focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus, as in the cocktail party effect Vision is the dominate sense An organized whole. An organization of the visual field into objects (figures) that stand out from their surroundings ( ground) Grouping Depth Perception Visual Cliff Binocular Cues Monocular Cues The perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into coherent groups Allows us to judge distance A device used to test infant depth perception Depth cue that involve 2 eyes. Ex. Retinal disparity and convergence Depth cue that only need 1 eye. Ex. Linear perspective Convergence A binocular depth cue that is achieved by the amount our eyes converge inward when looking at an object Retinal Disparity A binocular depth cue that is achieved by comparing images from 2 eyeballs Phi Phenomenon An illusion of movement created when two or more lights blink on and off Perceptual Constancy Perceiving objects as unchanging even as illumination and retinal images change Perceptual Adaption Perpetual Set In vision, the ability to adjust to an artificially displaced or even inverted visual field A mental predisposition to perceive on thing and not another. (UFOs) Human factors Psychology Explore and people and machines interact. Try to make technology easier for people to use Perception without sensory input Extrasensory Perception (ESP) Parapsychology People who study paranormal phenomenon, including ESP and psycho kinesis Telepathy Being able to send and receive messages through your mind Clairvoyance Perceiving remote events Precognition Perceiving future events Psychokinesis Mind over matter – being able to left things or move things with just your mind