Cells and Tissues - Brookwood High School
advertisement

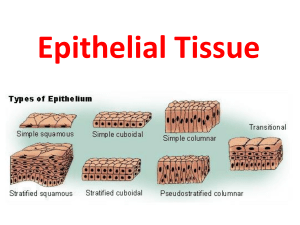
Tissue: Fabric of Life Read & Review Chapter 4 Body Tissues Histologytissues study of biology of tissues are cells organized for a specific function Development of Tissues Primary Germ Layers the process of forming 3 germ layers is called gastrulation the process of the germ layers differentiating into tissues is called histogenesis Tissue development Endoderm – innermost layer Mesoderm - middle layer ex. Lining of digestive and respiratory organs, thyroid ex. muscle, skeleton, blood, skin, connective tissue, excretory and reproductive organs Ectoderm – outermost layer ex. skin, nervous, epidermis tissue Tissues Groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Four primary tissue types 1. Epithelial Covering Support 2. Connective 3. Muscle Movement 4. Nervous Control II. Epithelial Tissues A. 2 Main Types 1. Membranous epithelium- lining/ covering 2. Glandular epithelium- secreting Epithelial: Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Protection- ex. skin Sensory- ex. skin, nose, eye, ear Secretion- ex. hormones, digestive juices, sweat Absorption- ex. small intestine, lungs Excretion- ex. urine, sweat C. Characteristics 1. limited extracellular space (matrix); cells appear tightly packed 2. apical surface (free surface exposed to the body exterior or the cavity of an internal organ) & basement membrane (bottom surface connected to connective tissue) Characteristics-(Continued) 3. avascular- no blood vessels; uses diffusion instead 4. innervated- contains nerve fibers 5. origin is ectodermal, mesodermal, endodermal 6. high regeneration capacity D. Classification of membranous epithelial 1. Cell Shapes a. Squamous- flat, round b. Cuboidal- cubed c. Columnar- narrow cylinder d. Pseudostratified- one layer of odd-shaped columnar cells; appears to be more than one layer Layers of Cells Layers of Cells a. Simple- single layer b. Stratified- more than one layer 3. Cell Shapes & Layers of Cells a. simple squamousex. alveoli in lungs b. simple cuboidalex. glands, kidney c. simple columnarex. golbet cells, cilia, microvilli Simple Squamous Epithelium Absorption Secretion Filtration Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Glands, ducts Walls of the kidney tubules Surface of the ovaries Simple Columnar Epithelium Goblet cells secrete mucus that aids in the function of respiratory system Pseudostratified columnar ex. goblet cells, respiratory All the cells rest on the basement membrane Since some of the cells are shorter then others, the nuclei appear at different heights Stratified Squamous (keratinized and non-keratinized) Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Most common stratified epithelium in the body Squamous at the free edge and columnar or cuboidal at the basement membrane Sites of abuse or friction: esophagus, mouth and outer portion of the skin, the outer surface of skin is keratinized (surface cells contain keratin, Keratinized vs. Nonkeratinized Stratified Cuboidal Stratified Cuboidal and Columnar Epithelium usually just two cell layers Fairly rare in the body; mainly ducts of large glands Sweat glands Mammary glands Transitional Epithelium highly modified stratified squamous: urinary bladder, ureters, urethra. All these organs are part of the urinary system and are subject to considerable stretching Section 2 vocab: common suffixes -ac, -al, -ary, -ic, -tic, -ous: pertaining to/related to -ad: derived from -algia: pain -cele: hernia -centesis: puncturing -ectomy: cutting out -iasis: a process or its results -itis: inflammation -ium: diminuitive, small -ize: to make into -lysis: break down -oid: resembling, like -oma: tumor/cancer -osis: denotes states or condition -ous: possessing, full of -plasty: molding, forming -rrhea: flow -sect: to cut, divide -sia, -sis, -tion, -y: action/condition -stomy: make an artificial opening -tomy: to cut Three Week Schedule 9/8- Gladular Epithelial tissue; Scope Work 9/9- Quiz (Epithelial tissue); Connective Tissue & Muscle tissue 9/10- Scope Work (Sub day) 9/11- Nervous Tissue; Scope Work 9/12- Vocab quiz (2); Microscope work (no lecture) 9/15- Integumentary Notes, Scope work 9/16- Integ. Notes, Tissues Review, Scope work 9/17- Tissue Practicum Quiz, Tissue Packet Due 9/18- Finish Integ Notes; Lab activity 9/19- Vocab Quiz (3), Disease & Disorder Lecture (End 1st 6 wks) 9/22- Review for Test 9/23- Tissue/IntegumentaryTest 9/24- Bones/Skeletal Lecture 9/25- Bones Discussion and Identification 9/26- Vocab Quiz (5), Bones Lab Glandular Epithelium Gland: one or more cells that make and secrete a product Secretion: protein molecule in aqueous fluid [some secrete a lipid or steroid rich secretion] Classification of glandular epithelial tissue 1. Cell Number a. Unicellular glands- single cells ex. goblet cells- mucus b. multicellular glands- clusters of cells; ex. mammary ducts- milk Classification of glandular epithelial tissue 2. Discharge method a. Exocrine glands – secrete into duct ex. saliva, sebaceous, mammary, sweat b. Endocrine glands - ductless; secrete hormones into bloodstream ex. pituitary gland, thyroid, ovary, testes, adrenal, pancreas Glandular Epithelium Endocrine: ( internal secreting) ductless; all hormone secretions directly into the blood or lymphatics (secrete by the process of exocytosis) thyroid; pituitary adrenals; Multicellular Exocrine Glands Two basic parts: Duct Secretory unit that consists of secretory cells called acini Modes of secretion Merocrine glandsexocytosis (pancreas, salivary glands, sweat glands) Holocrine Glandsrupture (Sebaceous oil glands of the skin) Epithelial tissue overview Epithelial Simple Squamous Cubodial Stratified Columnar Pseudostratified transitional ciliated cubodial nonciliated columnar ciliated squamous keratinized nonkeratinized nonciliated