Skeletal System 3
advertisement

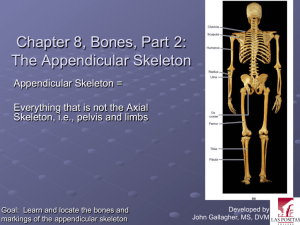
Skeletal System 3 Honors Anatomy to copy edition The Appendicular Skeleton The Pectoral Girdle (Shoulder) • 2 pectoral girdles • attach bones of upper limbs to axial skeleton • each: 1 clavicle • 1 scapula Clavicle • S-shaped, (medial ½ convex anteriorly, lateral ½ concave anteriorly) slender bone • lies horizontally across anterior thorax superior to 1st rib Clavicle • medial end = sternal end is rounded & articulates with the manubrium @ sternoclavicular joint Clavicle • lateral end = acromial end is flat • articulates with acromion of the scapula to form acromialclavicular joint Clavicle • last bone to stop growing • 1 of most frequently fx’d bones (2 curves) usually from fall on outstretched arm • or see compression fx in auto accidents from shoulder strap which can cause damage to median n. (between clavicle & 2nd rib) Scapula • aka shoulder blade, angel bone • large, triangular, flat bone • in superior part of posterior thorax between levels of 2nd & 7th ribs • spine: prominent ridge that runs diagonally across posterior surface Scapula • lateral edge: acromion a flattened expanded process, easily felt as hi pt of shoulder (tailors use it as landmark to measure length of arm) • glenoid cavity: inferior to acromion, smooth, shallow depression that accepts head of humerus in shoulder joint Upper Limb • 6 parts: 1. Humerus 2. Ulna 3. Radius 4. Carpals 5. Metacarpals 6. Phalanges • • • • • Joints: Shoulder Elbow Wrist Hand Humerus • longest & largest bone of upper limb • articulates proximally with scapula & distally with ulna & radius • head: rounded proximal end »articulates with glenoid cavity of scapula to form glenohumeral joint Humerus • distal end: • capitulum: rounded knob on lateral aspect that articulates with head of radius • trochlea: medial to capitulum, spool-shaped, articulates with ulna Ulna • medial aspect of forearm • longer than radius • proximal end: olecranon (prominence in elbow) • distal end: head, styloid process (posterior) Radius • lateral aspect of forearm • proximal end: head of radius: articulates with capitulum • distal end: styloid process (palpable proximal to thumb) Ulna & Radius • connect @ 3 places 1. interosseous membrane 2. proximal end 3. distal end Carpals • proximal to the hand, distal to radius & ulna • 8 small bones joined by ligaments • articulations w/each other called intercarpal joints Metacarpals Phalanges • 14 bones of the digits (each hand) • #’d I to V beginning with thumb • thumb is the pollex has only 2 phalanges, other digits have 3 • joints between phalanges called interphalangeal joints Pelvic Girdle • 2 hip bones (os coxa) which unite anteriorly at pubic symphysis and posteriorly with the sacrum @ sacroiliac joint Pelvic Girdle • Functions: • provides sturdy support for vertebral column • connects lower limb to axial skeleton Newborn Pelvis • 3 bones on each side: 1. Ilium – superior 2. Pubis – anterior & inferior 3. Ischium • posterior & inferior Ilium • largest of the 3 hip bones • distinguishing features: 1. Iliac Crest • along superior surface 1. Sacroiliac Joint (SI Joint) • between sacrum and ilium Ischium • ramus of ischium fuses with pubis • distinguishing features: 1. Ischial Tuberosity • what you feel when someone sits on your lap Pubis • Acetabulum – formed by ilium, ischium, & pubis – is the “socket” half of the hip joint • Pubic Symphysis – joint between the 2 hip bones True Pelvis/ False Pelvis • Pelvic Brim: line that distinguishes between true & false palvis Male Pelvis • generally male bone heavier & stronger & have larger surface marker (because larger muscles attach) • Pelvis: – deeper false pelvis, smaller, narrower – pelvic brim heart-shaped – acetabulum larger, faces posterior – obturator foramen round Female Pelvis • generally bones lighter & thinner • Pelvis: – false pelvis shallow, widers – pelvic brim larger, more oval – acetabulum smaller & faces anterior – obturator foramen oval Lower Limb • • • • • • • • 30 bones in each: 1 femur 1 patella 1 tibia 1 fibula 7 tarsals 5 metatarsals 14 phalanges Femur • longest, heaviest, & strongest bone in the body • proximally articulates with the acetabulum to form hip joint – Head of the Femur: “ball” part of joint • small, central depression: fovea capitis – Greater Trochanter • prominence felt & seen @ side of hip Patella (kneecap) • small, triangular, sesamoid bone • develops in tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle • Parts: • Base: broad, superior end • Apex: pointed, inferior end Tibia “shin bone” larger, medial, weight-bearing bone of lower leg proximally articulates with femur & fibula distally articulates with fibula & tarsals Tibia • medial malleolus forms prominence that is palpable & visible on medial ankle Fibula • parallel & lateral to the tibia & considerably smaller • head of fibula on proximal end • lateral malleolus at distal end Tarsals • 7 bones: • 1 calcaneous: heel bone, largest of the tarsals Metatarsals • 5 bones between tarsals & phalanges • #’d I to V from medial lateral Arches of the Foot • 2 arches in foot: 1. allows the foot to support weight of body by distributing weight over the soft & hard tissues 2. provide leverage while walking fully developed by age 12 - 13 Arches of the Foot • 2 longitudinal arches (medial & lateral • 1 transverse arch Development of the Skeletal • all skeletal tissue arises from System mesoderm • 1st bone: skull in 4th wk • U/S ~ 24 – 25 wks: 1. Clubfoot: Medical Terminology – inherited deformity in which baby is born with foot twisted inferiorly & medially – 1/1000 births – tx: casts or wraps, surgery may be indicated Medical Terminology 2. Genu valgum: • knees abnormally close together with increased space between ankles • aka “knock-knee”